A programmable pAgo nuclease with RNA target-cleavage specificity from the mesophilic bacterium Verrucomicrobia
- PMID: 37431184
- PMCID: PMC10448046
- DOI: 10.3724/abbs.2023110
A programmable pAgo nuclease with RNA target-cleavage specificity from the mesophilic bacterium Verrucomicrobia
Abstract
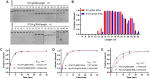
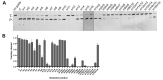
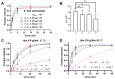
Argonaute (Ago) proteins are conserved programmable nucleases present in eukaryotes and prokaryotes and provide defense against mobile genetic elements. Almost all characterized pAgos prefer to cleave DNA targets. Here, we describe a novel pAgo from Verrucomicrobia bacterium (VbAgo) that can specifically cleave RNA targets rather than DNA targets at 37°C and function as a multiple-turnover enzyme showing prominent catalytic capacity. VbAgo utilizes DNA guides (gDNAs) to cleave RNA targets at the canonical cleavage site. Meanwhile, the cleavage activity is remarkably strengthened at low concentrations of NaCl. In addition, VbAgo presents a weak tolerance for mismatches between gDNAs and RNA targets, and single-nucleotide mismatches at positions 11‒12 and dinucleotide mismatches at positions 3‒15 dramatically reduce target cleavage. Moreover, VbAgo can efficiently cleave highly structured RNA targets at 37°C. These properties of VbAgo broaden our understanding of Ago proteins and expand the pAgo-based RNA manipulation toolbox.
Keywords: RNA target specificity; bacterium; programmable nucleases; prokaryotic argonaute.
Conflict of interest statement
Hubei University has applied for a patent (application No. 202210794665.9) for the application of VbAgo with L. Ma, Q. Liu, Y. Liu, F. Wang and W. Chen listed as co-inventors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A programmable pAgo nuclease with RNA target preference from the psychrotolerant bacterium Mucilaginibacter paludis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 May 20;50(9):5226-5238. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac315. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35524569 Free PMC article.
-
Programmable RNA targeting by bacterial Argonaute nucleases with unconventional guide binding and cleavage specificity.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 8;13(1):4624. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32079-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35941106 Free PMC article.
-
A programmable omnipotent Argonaute nuclease from mesophilic bacteria Kurthia massiliensis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Feb 22;49(3):1597-1608. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1278. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33444443 Free PMC article.
-
A long look at short prokaryotic Argonautes.Trends Cell Biol. 2023 Jul;33(7):605-618. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2022.10.005. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Trends Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36428175 Review.
-
Argonaute proteins confer immunity in all domains of life.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2023 Aug;74:102313. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2023.102313. Epub 2023 Apr 4. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37023508 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of argonaute nucleases from mesophilic bacteria Pseudobutyrivibrio ruminis.Bioresour Bioprocess. 2024 Oct 7;11(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s40643-024-00797-x. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2024. PMID: 39373873 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro programmable DNA cleavage by a eukaryotic Argonaute.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jun 20;53(12):gkaf561. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf561. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40548933 Free PMC article.
-
Mn2+-induced structural flexibility enhances the entire catalytic cycle and the cleavage of mismatches in prokaryotic argonaute proteins.Chem Sci. 2024 Mar 14;15(15):5612-5626. doi: 10.1039/d3sc06221j. eCollection 2024 Apr 17. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38638240 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swarts DC, Makarova K, Wang Y, Nakanishi K, Ketting RF, Koonin EV, Patel DJ, et al. The evolutionary journey of Argonaute proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol. . 2014;21:743–753. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2879. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Makarova KS, Wolf YI, van der Oost J, Koonin EV. Prokaryotic homologs of Argonaute proteins are predicted to function as key components of a novel system of defense against mobile genetic elements. Biol Direct. . 2009;4:29. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-4-29. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lisitskaya L, Aravin AA, Kulbachinskiy A. DNA interference and beyond: structure and functions of prokaryotic Argonaute proteins. Nat Commun. . 2018;9:5165. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07449-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

