Optimized Replication of Arrayed Bacterial Mutant Libraries Increases Access to Biological Resources
- PMID: 37432110
- PMCID: PMC10434011
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01693-23
Optimized Replication of Arrayed Bacterial Mutant Libraries Increases Access to Biological Resources
Abstract
Biological collections, including arrayed libraries of single transposon (Tn) or deletion mutants, greatly accelerate the pace of bacterial genetic research. Despite the importance of these resources, few protocols exist for the replication and distribution of these materials. Here, we describe a protocol for creating multiple replicates of an arrayed bacterial Tn library consisting of approximately 6,800 mutants in 96-well plates (73 plates). Our protocol provides multiple checkpoints to guard against contamination and minimize genetic drift caused by freeze/thaw cycles. This approach can also be scaled for arrayed culture collections of various sizes. Overall, this protocol is a valuable resource for other researchers considering the construction and distribution of arrayed culture collection resources for the benefit of the greater scientific community. IMPORTANCE Arrayed mutant collections drive robust genetic screens, but few protocols exist for replication of these resources and subsequent quality control. Increasing the distribution of arrayed biological collections will increase the accessibility and use of these resources. Developing standardized techniques for replication of these resources is essential for ensuring their quality and usefulness to the scientific community.
Keywords: Enterococcus faecalis; biological collections; functional genomics; genetic tools; scientific rigor; transposon mutagenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

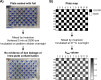
Update of
-
Optimized replication of arrayed bacterial mutant libraries increase access to biological resources.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 25:2023.04.25.537918. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.25.537918. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0169323. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01693-23. PMID: 37162974 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Optimized replication of arrayed bacterial mutant libraries increase access to biological resources.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 25:2023.04.25.537918. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.25.537918. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0169323. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01693-23. PMID: 37162974 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Genome-Wide Mutagenesis in Borrelia burgdorferi.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1690:201-223. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7383-5_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29032547
-
Randomly barcoded transposon mutant libraries for gut commensals I: Strategies for efficient library construction.Cell Rep. 2024 Jan 23;43(1):113517. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113517. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38142397 Review.
-
Comprehensive Functional Analysis of the Enterococcus faecalis Core Genome Using an Ordered, Sequence-Defined Collection of Insertional Mutations in Strain OG1RF.mSystems. 2018 Sep 11;3(5):e00062-18. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00062-18. eCollection 2018 Sep-Oct. mSystems. 2018. PMID: 30225373 Free PMC article.
-
Randomly barcoded transposon mutant libraries for gut commensals II: Applying libraries for functional genetics.Cell Rep. 2024 Jan 23;43(1):113519. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113519. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38142398 Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of an arrayed CRISPRi library as a resource for essential gene function studies in Streptococcus mutans.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jan 11;12(1):e0314923. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03149-23. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38054713 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into ecology, pathogenesis, and biofilm formation of Enterococcus faecalis from functional genomics.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2025 Mar 27;89(1):e0008123. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00081-23. Epub 2024 Dec 23. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39714182 Review.
References
-
- Koo B-M, Kritikos G, Farelli JD, Todor H, Tong K, Kimsey H, Wapinski I, Galardini M, Cabal A, Peters JM, Hachmann A-B, Rudner DZ, Allen KN, Typas A, Gross CA. 2017. Construction and analysis of two genome-scale deletion libraries for Bacillus subtilis. Cell Syst 4:291–305.e7. doi:10.1016/j.cels.2016.12.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goodall ECA, Morris FC, McKeand SA, Sullivan R, Warner IA, Sheehan E, Boelter G, Icke C, Cunningham AF, Cole JA, Banzhaf M, Bryant JA, Henderson IR. 2022. LI-detector: a method for curating ordered gene-replacement libraries. Microbiol Spectr 10:e00833-22. doi:10.1128/spectrum.00833-22. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dale JL, Beckman KB, Willett JLE, Nilson JL, Palani NP, Baller JA, Hauge A, Gohl DM, Erickson R, Manias DA, Sadowsky MJ, Dunny GM. 2018. Comprehensive functional analysis of the Enterococcus faecalis core genome using an ordered, sequence-defined collection of insertional mutations in strain OG1RF. mSystems 3:e00062-18. doi:10.1128/mSystems.00062-18. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

