Targeting Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway by Flavonoids: Implication for Cancer Therapeutics
- PMID: 37432240
- PMCID: PMC10181252
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15092088
Targeting Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway by Flavonoids: Implication for Cancer Therapeutics
Abstract
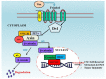
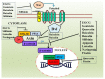
The Wnt pathway has been recognized for its crucial role in human development and homeostasis, but its dysregulation has also been linked to several disorders, including cancer. Wnt signaling is crucial for the development and metastasis of several kinds of cancer. Moreover, members of the Wnt pathway have been proven to be effective biomarkers and promising cancer therapeutic targets. Abnormal stimulation of the Wnt signaling pathway has been linked to the initiation and advancement of cancer in both clinical research and in vitro investigations. A reduction in cancer incidence rate and an improvement in survival may result from targeting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. As a result, blocking this pathway has been the focus of cancer research, and several candidates that can be targeted are currently being developed. Flavonoids derived from plants exhibit growth inhibitory, apoptotic, anti-angiogenic, and anti-migratory effects against various malignancies. Moreover, flavonoids influence different signaling pathways, including Wnt, to exert their anticancer effects. In this review, we comprehensively evaluate the influence of flavonoids on cancer development and metastasis by focusing on the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, and we provide evidence of their impact on a number of molecular targets. Overall, this review will enhance our understanding of these natural products as Wnt pathway modulators.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin signaling; anticancer; flavonoids; natural product.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Flavonoids and Wnt/β-catenin signaling: potential role in colorectal cancer therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Jul 8;15(7):12094-106. doi: 10.3390/ijms150712094. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25007066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting lncRNA/Wnt axis by flavonoids: A promising therapeutic approach for colorectal cancer.Phytother Res. 2022 Nov;36(11):4024-4040. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7550. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Phytother Res. 2022. PMID: 36227024 Review.
-
Flavonoids: potential Wnt/beta-catenin signaling modulators in cancer.Life Sci. 2011 Oct 10;89(15-16):545-54. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2011.05.003. Epub 2011 May 18. Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21635906 Review.
-
Wnt/β-catenin mediated signaling pathways in cancer: recent advances, and applications in cancer therapy.Mol Cancer. 2025 Jun 10;24(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02363-1. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40495229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt pathway modulators in cancer therapeutics: An update on completed and ongoing clinical trials.Int J Cancer. 2022 Mar 1;150(5):727-740. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33811. Epub 2021 Oct 11. Int J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34536299 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Insight into Prostate Cancer: Preventive Role of Selective Bioactive Molecules.Life (Basel). 2023 Sep 27;13(10):1976. doi: 10.3390/life13101976. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling role of oncogenic signalling pathways in complicating breast cancer.Biomedicine (Taipei). 2025 Mar 1;15(1):13-21. doi: 10.37796/2211-8039.1640. eCollection 2025. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2025. PMID: 40176859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the Role of OCT4 in Cancer Lineage Plasticity: A Cross-Cancer Perspective with an Emphasis on Prostate Cancer.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 4;13(7):1642. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071642. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sinensetin suppresses breast cancer cell progression via Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibition.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jan 31;13(1):348-362. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-1317. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38410229 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-metastatic Effect of Heliotropium bacciferum on MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cell Line.Cureus. 2024 Apr 24;16(4):e58939. doi: 10.7759/cureus.58939. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38800305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taheri N., Choi E.L., Nguyen V.T.T., Chandra A., Hayashi Y. Wnt Signaling in the Gastrointestinal Tract in Health and Disease. Physiologia. 2023;3:86–97. doi: 10.3390/physiologia3010007. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

