Clinical and Economic Outcomes in Patients With Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma Receiving First-Line Systemic Treatment (the IMPACT UC I Study)
- PMID: 37432283
- PMCID: PMC10485286
- DOI: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad174
Clinical and Economic Outcomes in Patients With Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma Receiving First-Line Systemic Treatment (the IMPACT UC I Study)
Abstract
Background: The IMPACT UC I study assessed real-world treatment patterns, outcomes, healthcare resource utilization (HCRU), and costs in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma (mUC) receiving first-line (1L) systemic treatment after the FDA approval of 1L immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) monotherapy.
Patients and methods: This retrospective study used 100% Medicare fee-for-service claims from 1/1/2015 to 6/30/2019 to identify patients aged ≥18 years diagnosed with UC with evidence of metastatic disease, continuously enrolled for 6 months before and after initial diagnosis. Patients were grouped by 1L treatment: cisplatin-containing chemotherapy, carboplatin-containing chemotherapy, ICI monotherapy, or nonplatinum-containing therapy. Unadjusted time on 1L treatment (TOT), overall survival (OS), HCRU, and total healthcare costs were analyzed.
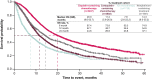
Results: Of 18 888 patients with mUC, 8630 (45.7%) had received identified 1L systemic treatment; platinum-containing chemotherapy was the most common (cisplatin-containing chemotherapy, 37.6%; carboplatin-containing chemotherapy, 30.2%). Cisplatin- and carboplatin-containing chemotherapy had the shortest time-to-treatment initiation (median, 1.7-3.0 months) and longest TOT (median, 4.0-4.3 months). Median OS was longest with cisplatin-containing chemotherapy (20.0 months) and shortest with ICI monotherapy (7.6 months). Cisplatin- and carboplatin-containing chemotherapy were associated with highest HCRU; total healthcare costs were approximately 2-fold higher with ICI monotherapy vs other 1L treatments ($10 359 vs $5042-$5709 per patient per month).
Conclusion: 1L platinum-containing chemotherapy resulted in the longest median OS and highest HCRU, whereas 1L ICI treatment had the shortest median OS and the highest costs. Over 50% of patients diagnosed with advanced UC (aUC) received no systemic therapy, highlighting the importance of optimal 1L treatment decisions in aUC.
Keywords: Medicare; first-line treatment; healthcare resource utilization; immune checkpoint inhibitors; metastatic urothelial carcinoma; treatment patterns.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Mehmet A. Bilen received research grants from Xencor (Institution), Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb (Institution), Genentech/Roche (Institution), Seattle Genetics (Institution), Incyte (Institution), Nektar (Institution), AstraZeneca (Institution), Tricon Pharmaceuticals (Institution), Genome & Company (Institution), AAA (Institution), Peloton Therapeutics (Institution), and Pfizer (Institution); and had an advisory role for Exelixis, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Calithera Biosciences, Genomic Health, Nektar, and Sanofi. Scott B. Robinson, Amy Schroeder, and Jing Peng are employees of Avalere Health and paid consultants of EMD Serono, Inc., Rockland, MA, USA, an affiliate of Merck KGaA. Ruth Kim is an employee of Pfizer and has stocks/shares in Exelixis and Bristol Myers Squibb. Frank X. Liu was an employee of EMD Serono, Inc., Rockland, MA, USA, an affiliate of Merck KGaA, at the time the study was conducted, and holds stocks in Merck. Abhijeet Bhanegaonkar is an employee of EMD Serono, Inc., Rockland, MA, USA, an affiliate of Merck KGaA and holds stocks in Merck.
Figures

References
-
- National Cancer Institute. SEER Cancer Stat Facts: Bladder Cancer. Accessed December 20, 2022. https://www.seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/urinb.html.
-
- American Cancer Society. Bladder cancer risk factors. Accessed December 20, 2022. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/bladder-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/ris....
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Bladder Cancer v2. 2022. Plymouth Meeting, PA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

