IL-6 selectively suppresses cDC1 specification via C/EBPβ
- PMID: 37432392
- PMCID: PMC10336151
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20221757
IL-6 selectively suppresses cDC1 specification via C/EBPβ
Abstract
Cytokines produced in association with tumors can impair antitumor immune responses by reducing the abundance of type 1 conventional dendritic cells (cDC1), but the mechanism remains unclear. Here, we show that tumor-derived IL-6 generally reduces cDC development but selectively impairs cDC1 development in both murine and human systems through the induction of C/EBPβ in the common dendritic cell progenitor (CDP). C/EBPβ and NFIL3 compete for binding to sites in the Zeb2 -165 kb enhancer and support or repress Zeb2 expression, respectively. At homeostasis, pre-cDC1 specification occurs upon Nfil3 induction and consequent Zeb2 suppression. However, IL-6 strongly induces C/EBPβ expression in CDPs. Importantly, the ability of IL-6 to impair cDC development is dependent on the presence of C/EBPβ binding sites in the Zeb2 -165 kb enhancer, as this effect is lost in Δ1+2+3 mutant mice in which these binding sites are mutated. These results explain how tumor-associated IL-6 suppresses cDC1 development and suggest therapeutic approaches preventing abnormal C/EBPβ induction in CDPs may help reestablish cDC1 development to enhance antitumor immunity.
© 2023 Kim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures




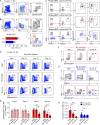

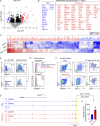


References
-
- Auffray, C., Fogg D.K., Narni-Mancinelli E., Senechal B., Trouillet C., Saederup N., Leemput J., Bigot K., Campisi L., Abitbol M., et al. 2009. CX3CR1+ CD115+ CD135+ common macrophage/DC precursors and the role of CX3CR1 in their response to inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 206:595–606. 10.1084/jem.20081385 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bagadia, P., Huang X., Liu T.T., Durai V., Grajales-Reyes G.E., Nitschké M., Modrusan Z., Granja J.M., Satpathy A.T., Briseño C.G., et al. 2019. An Nfil3-Zeb2-Id2 pathway imposes Irf8 enhancer switching during cDC1 development. Nat. Immunol. 20:1174–1185. 10.1038/s41590-019-0449-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

