Colorectal cancer-secreted exosomal circ_001422 plays a role in regulating KDR expression and activating mTOR signaling in endothelial cells by targeting miR-195-5p
- PMID: 37432457
- PMCID: PMC11797106
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-05095-1
Colorectal cancer-secreted exosomal circ_001422 plays a role in regulating KDR expression and activating mTOR signaling in endothelial cells by targeting miR-195-5p
Abstract
Background: As non-coding RNAs, exosomal circular RNAs (circRNAs) regulate colorectal cancer (CRC) progression, although the functional mechanisms by which such molecules affect the tumor microenvironment are still elusive. Herein, we aimed to explore the potential clinical significance of a signature of five serum-derived circRNAs in CRC and investigated the mechanisms underlying endothelial cell angiogenesis mediated by CRC-secreted exosomal circ_001422.
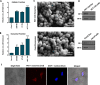
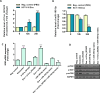
Methods: The expression of a signature of five serum-derived circRNAs (circ_0004771, circ_0101802, circ_0082333, circ_0072309, and circ_001422) were measured by RT-qPCR, and their associations with tumor staging and lymph node metastasis were further evaluated in CRC patients. In silico analysis was used to show the relationship between circ_001422, miR-195-5p, and KDR, validated by dual-luciferase reporter and Western blotting assays. CRC cell-derived exosomes were isolated and characterized by scanning electron microscopy and Western blotting. Endothelial cell uptake of PKH26-labeled exosomes was demonstrated using a spectral confocal microscope. In vitro genetic strategies were used to exogenously alter the expression level of circ_001422 and miR-195-5p expression. Cell proliferation assay, transwell migration assay, and capillary tube formation assay were conducted to explore the role of CRC-secreted exosomal circ_001422 in endothelial cell function in vitro.
Results: The expression levels of serum-derived circ_0004771, circ_0101802, circ_0082333, and circ_001422 were significantly higher in CRC and were positively correlated with the lymph node metastasis status. However, circ_0072309 showed a significant down-regulation in CRC than in healthy individuals. Furthermore, a higher expression level of circ_001422 in both cellular and exosomal fractions was found in HCT-116 CRC cells. We found that HCT-116 exosomes considerably enhanced proliferation and migration of endothelial cells through shuttling of circ_001422. We also observed that exosomes derived from HCT-116 cell, but not non-aggressive Caco-2 CRC cells, increased in vitro tubulogenesis of endothelial cells. Importantly, knockdown of circ_001422 impaired the capability of endothelial cells to form the capillary-like tube structures. CRC-secreted circ_001422 acted as an endogenous miR-195-5p sponge to inhibit miR-195-5p activity, which led to increased KDR expression and mTOR signaling activation in endothelial cells. Importantly, ectopic expression of miR-195-5p mimicked the effect of circ_001422 silencing on KDR/mTOR signaling in endothelial cells.
Conclusion: This study attributed a biomarker role for circ_001422 in CRC diagnosis and proposed a novel mechanism whereby circ_001422 up-regulates KDR through sponging miR-195-5p. These interactions may give rise to the activation of mTOR signaling and may be a possible clarification for the pro-angiogenesis effects of CRC-secreted exosomal circ_001422 on endothelial cells.
Keywords: Circ_001422; Colorectal cancer; Endothelial cell angiogenesis; Exosomes; miR-195-5p.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
circ-NOLC1 inhibits the development of cervical cancer by regulating miR-330-5p-PALM signaling axis.Hereditas. 2025 Jun 18;162(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00478-5. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 40533863 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0084927 promotes progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma by sponging miR-4725-5p to activate the PDPK1/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Cell Signal. 2025 Oct;134:111965. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111965. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 40581264
-
Exosomal miR-382-5p prevents pre-metastatic niche formation by inhibiting GPR176/GNAS-CXCR1/CXCR2 axis in colorectal cancer liver metastasis.Cell Signal. 2025 Oct;134:111963. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111963. Epub 2025 Jun 25. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 40578589
-
MicroRNAs that regulate PTEN as potential biomarkers in colorectal cancer: a systematic review.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 Apr;146(4):809-820. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03172-3. Epub 2020 Mar 7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32146564 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
Cited by
-
Melanoma cell line-derived exosomal miR-424-5p: a key promoter of angiogenesis through LATS2 interaction.Oncol Res. 2025 Jan 16;33(2):357-367. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.050878. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 39866229 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs in human diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Sep 4;5(9):e699. doi: 10.1002/mco2.699. eCollection 2024 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39239069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal microRNAs in lung cancer: a narrative review.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 30;13(6):3090-3105. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-2319. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38988916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding pre-metastatic niche formation: implications for colorectal cancer liver metastasis.J Transl Med. 2025 Mar 17;23(1):340. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06328-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40098140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes derived from colorectal cancer cells take part in activation of stromal fibroblasts through regulating PHLPP isoforms.EXCLI J. 2024 May 2;23:634-654. doi: 10.17179/excli2024-6926. eCollection 2024. EXCLI J. 2024. PMID: 38887393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almouh M, Razmara E, Bitaraf A, Ghazimoradi MH, Hassan ZM, Babashah S (2022) Circular RNAs play roles in regulatory networks of cell signaling pathways in human cancers. Life Sci 309:120975 - PubMed
-
- Babashah S, Soleimani M (2011) The oncogenic and tumour suppressive roles of microRNAs in cancer and apoptosis. Eur J Cancer 47:1127–1137 - PubMed
-
- Bayat A, Raad M, Sharafshah A, Ahmadvand M, Aminian H (2022) Identification of miR-195-5p as a novel prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. Mol Biol Rep 49:6453–6457 - PubMed
-
- Buccafusca G, Proserpio I, Tralongo AC, Giuliano SR, Tralongo P (2019) Early colorectal cancer: diagnosis, treatment and survivorship care. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 136:20–30 - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Shan G (2021) CircRNA in cancer: fundamental mechanism and clinical potential. Cancer Lett 505:49–57 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

