A data-driven study of Alzheimer's disease related amyloid and tau pathology progression
- PMID: 37433038
- PMCID: PMC10690020
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awad232
A data-driven study of Alzheimer's disease related amyloid and tau pathology progression
Abstract
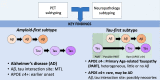
Amyloid-β is thought to facilitate the spread of tau throughout the neocortex in Alzheimer's disease, though how this occurs is not well understood. This is because of the spatial discordance between amyloid-β, which accumulates in the neocortex, and tau, which accumulates in the medial temporal lobe during ageing. There is evidence that in some cases amyloid-β-independent tau spreads beyond the medial temporal lobe where it may interact with neocortical amyloid-β. This suggests that there may be multiple distinct spatiotemporal subtypes of Alzheimer's-related protein aggregation, with potentially different demographic and genetic risk profiles. We investigated this hypothesis, applying data-driven disease progression subtyping models to post-mortem neuropathology and in vivo PET-based measures from two large observational studies: the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) and the Religious Orders Study and Rush Memory and Aging Project (ROSMAP). We consistently identified 'amyloid-first' and 'tau-first' subtypes using cross-sectional information from both studies. In the amyloid-first subtype, extensive neocortical amyloid-β precedes the spread of tau beyond the medial temporal lobe, while in the tau-first subtype, mild tau accumulates in medial temporal and neocortical areas prior to interacting with amyloid-β. As expected, we found a higher prevalence of the amyloid-first subtype among apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 allele carriers while the tau-first subtype was more common among APOE ε4 non-carriers. Within tau-first APOE ε4 carriers, we found an increased rate of amyloid-β accumulation (via longitudinal amyloid PET), suggesting that this rare group may belong within the Alzheimer's disease continuum. We also found that tau-first APOE ε4 carriers had several fewer years of education than other groups, suggesting a role for modifiable risk factors in facilitating amyloid-β-independent tau. Tau-first APOE ε4 non-carriers, in contrast, recapitulated many of the features of primary age-related tauopathy. The rate of longitudinal amyloid-β and tau accumulation (both measured via PET) within this group did not differ from normal ageing, supporting the distinction of primary age-related tauopathy from Alzheimer's disease. We also found reduced longitudinal subtype consistency within tau-first APOE ε4 non-carriers, suggesting additional heterogeneity within this group. Our findings support the idea that amyloid-β and tau may begin as independent processes in spatially disconnected regions, with widespread neocortical tau resulting from the local interaction of amyloid-β and tau. The site of this interaction may be subtype-dependent: medial temporal lobe in amyloid-first, neocortex in tau-first. These insights into the dynamics of amyloid-β and tau may inform research and clinical trials that target these pathologies.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; PART; PET imaging; data-driven subtyping; neuropathology.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests.
Figures
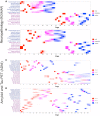
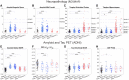

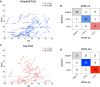
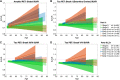
References
-
- Bloom GS. Amyloid-β and tau: The trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol. 2014;71:505–508. - PubMed
-
- Hardy JA, Higgins GA. Alzheimer’s disease: The amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science. 1992;256:184–185. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 1991;6:487–498. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Frequency of stages of Alzheimer-related lesions in different age categories. Neurobiol Aging. 1997;18:351–357. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Thal DR, Ghebremedhin E, Del Tredici K. Stages of the pathologic process in Alzheimer disease: Age categories from 1 to 100 years. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2011;70:960–969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

