Nanoscaled Discovery of a Shunt Rifamycin from Salinispora arenicola Using a Three-Color GFP-Tagged Staphylococcus aureus Macrophage Infection Assay
- PMID: 37433130
- PMCID: PMC10425972
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00049
Nanoscaled Discovery of a Shunt Rifamycin from Salinispora arenicola Using a Three-Color GFP-Tagged Staphylococcus aureus Macrophage Infection Assay
Abstract
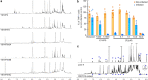
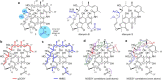
Antimicrobial resistance has emerged as a global public health threat, and development of novel therapeutics for treating infections caused by multi-drug resistant bacteria is urgent. Staphylococcus aureus is a major human and animal pathogen, responsible for high levels of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The intracellular survival of S. aureus in macrophages contributes to immune evasion, dissemination, and resilience to antibiotic treatment. Here, we present a confocal fluorescence imaging assay for monitoring macrophage infection by green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged S. aureus as a front-line tool to identify antibiotic leads. The assay was employed in combination with nanoscaled chemical analyses to facilitate the discovery of a new, active rifamycin analogue. Our findings indicate a promising new approach for the identification of antimicrobial compounds with macrophage intracellular activity. The antibiotic identified here may represent a useful addition to our armory in tackling the silent pandemic of antimicrobial resistance.
Keywords: Salinispora arenicola; Staphylococcus aureus; fluorescence imaging assay; macrophage; rifamycin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy of novel rifamycin derivatives against rifamycin-sensitive and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in murine models of infection.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Nov;50(11):3658-64. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01087-05. Epub 2006 Aug 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16940074 Free PMC article.
-
Rifamycin Derivatives Are Effective Against Staphylococcal Biofilms In Vitro and Elutable From PMMA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Sep;473(9):2874-84. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4300-3. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 25896136 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental evolution of Staphylococcus aureus in macrophages: dissection of a conditional adaptive trait promoting intracellular survival.mBio. 2024 Jun 12;15(6):e0034624. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00346-24. Epub 2024 Apr 29. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38682911 Free PMC article.
-
The Complex Intracellular Lifecycle of Staphylococcus aureus Contributes to Reduced Antibiotic Efficacy and Persistent Bacteremia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 12;25(12):6486. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126486. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staph wars: the antibiotic pipeline strikes back.Microbiology (Reading). 2023 Sep;169(9):001387. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001387. Microbiology (Reading). 2023. PMID: 37656158 Free PMC article. Review.

