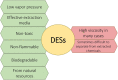
The Most Potent Natural Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics, and Food Ingredients Isolated from Plants with Deep Eutectic Solvents
- PMID: 37433265
- PMCID: PMC10375538
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c01656
The Most Potent Natural Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics, and Food Ingredients Isolated from Plants with Deep Eutectic Solvents
Abstract
There is growing interest in reducing the number of synthetic products or additives and replacing them with natural ones. The pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries are especially focused on natural and bioactive chemicals isolated from plants or microorganisms. The main challenge here is to develop efficient and ecological methods for their isolation. According to the strategies and rules of sustainable development and green chemistry, green solvents and environmentally friendly technologies must be used. The application of deep eutectic solvents as efficient and biodegradable solvents seems to be a promising alternative to traditional methods. They are classified as being green and ecological but, most importantly, very efficient extraction media compared to organic solvents. The aim of this review is to present the recent findings on green extraction, as well as the biological activities and the possible applications of natural plant ingredients, namely, phenolics, flavonoids, terpenes, saponins, and some others. This paper thoroughly reviews modern, ecological, and efficient extraction methods with the use of deep eutectic solvents (DESs). The newest findings, as well as the factors influencing the efficiency of extraction, such as water content, and hydrogen bond donor and acceptor types, as well as the extraction systems, are also discussed. New solutions to the major problem of separating DESs from the extract and for solvent recycling are also presented.
Keywords: bioactive compounds from plants; bioactive ingredients in cosmetics; deep eutectic solvents; green solvents; natural food additives; natural pharmaceuticals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Juneidi I.; Hayyan M.; Hashim M. A. Evaluation of Toxicity and Biodegradability for Cholinium-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5 (102), 83636–83647. 10.1039/C5RA12425E. - DOI
-
- Wang Z.; Li S.; Li T.; Hu T.; Ge X. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) for Green Recycling of Wasted Lithium-Ion Batteries (LIBs): Progress on Pushing the Overall Efficiency. Min. Metall. Explor. 2022, 39, 2149–2165. 10.1007/s42461-022-00660-7. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources