Toll-like receptor 5 tunes hepatic and pancreatic stellate cells activation
- PMID: 37433685
- PMCID: PMC10347502
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgast-2023-001148
Toll-like receptor 5 tunes hepatic and pancreatic stellate cells activation
Abstract
Objective: Stellate cells are responsible for liver and pancreas fibrosis and strictly correlate with tumourigenesis. Although their activation is reversible, an exacerbated signalling triggers chronic fibrosis. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) modulate stellate cells transition. TLR5 transduces the signal deriving by the binding to bacterial flagellin from invading mobile bacteria.
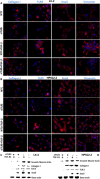
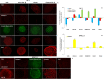
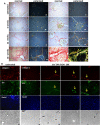
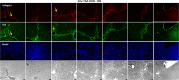
Design: Human hepatic and pancreatic stellate cells were activated by the administration of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β). TLR5 was transiently knocked down by short-interference RNA transfection. Reverse Transcription-quantitativePCR and western blot were performed to analyse the transcript and protein level of TLR5 and the transition players. Fluorescence microscopy was performed to identify these targets in spheroids and in the sections of murine fibrotic liver.
Results: TGF-β-activated human hepatic and pancreatic stellate cells showed an increase of TLR5 expression. TLR5 knockdown blocked the activation of those stellate cells. Furthermore, TLR5 busted during murine liver fibrosis and co-localised with the inducible Collagen I. Flagellin suppressed TLR5, COL1A1 and ACTA2 expression after the administration of TGF-β. Instead, the antagonist of TLR5 did not block the effect of TGF-β. Wortmannin, a specific AKT inhibitor, induced TLR5 but not COL1A1 and ACTA2 transcript and protein level.
Conclusion: TGF-β-mediated activation of hepatic and pancreatic stellate cells requires the over-expression of TLR5. Instead, its autonomous signalling inhibits the activation of the stellate cells, thus prompting a signalling through different regulatory pathways.
Keywords: CELL SIGNALLING; GASTROINTESTINAL PATHOLOGY; HEPATIC FIBROSIS; HEPATIC STELLATE CELL; PANCREATIC FIBROSIS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
