At a glance: the largest Niemann-Pick type C1 cohort with 602 patients diagnosed over 15 years
- PMID: 37433892
- PMCID: PMC10545733
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-023-01408-7
At a glance: the largest Niemann-Pick type C1 cohort with 602 patients diagnosed over 15 years
Abstract
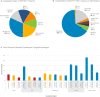
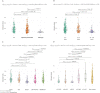
Niemann-Pick type C1 disease (NPC1 [OMIM 257220]) is a rare and severe autosomal recessive disorder, characterized by a multitude of neurovisceral clinical manifestations and a fatal outcome with no effective treatment to date. Aiming to gain insights into the genetic aspects of the disease, clinical, genetic, and biomarker PPCS data from 602 patients referred from 47 countries and diagnosed with NPC1 in our laboratory were analyzed. Patients' clinical data were dissected using Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) terms, and genotype-phenotype analysis was performed. The median age at diagnosis was 10.6 years (range 0-64.5 years), with 287 unique pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) variants identified, expanding NPC1 allelic heterogeneity. Importantly, 73 P/LP variants were previously unpublished. The most frequent variants detected were: c.3019C > G, p.(P1007A), c.3104C > T, p.(A1035V), and c.2861C > T, p.(S954L). Loss of function (LoF) variants were significantly associated with earlier age at diagnosis, highly increased biomarker levels, and a visceral phenotype (abnormal abdomen and liver morphology). On the other hand, the variants p.(P1007A) and p.(S954L) were significantly associated with later age at diagnosis (p < 0.001) and mildly elevated biomarker levels (p ≤ 0.002), consistent with the juvenile/adult form of NPC1. In addition, p.(I1061T), p.(S954L), and p.(A1035V) were associated with abnormality of eye movements (vertical supranuclear gaze palsy, p ≤ 0.05). We describe the largest and most heterogenous cohort of NPC1 patients published to date. Our results suggest that besides its utility in variant classification, the biomarker PPCS might serve to indicate disease severity/progression. In addition, we establish new genotype-phenotype relationships for "frequent" NPC1 variants.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
PGM, LMP, CP, SS, DV, LSA, CJ, HH, CCYL, AL, GTM, SO, M-II, SF, T-MS, NV, CC, KKK, JPB, TB, PB, and AB-A are employees of Centogene GmbH.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic and phenotypic variability in adult patients with Niemann Pick type C from Serbia: single-center experience.J Neurol. 2022 Jun;269(6):3167-3174. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10918-7. Epub 2022 Jan 7. J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34993563
-
[Niemann-Pick type C disease and psychosis: Two siblings].Encephale. 2015 Jun;41(3):238-43. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2014.08.007. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Encephale. 2015. PMID: 25238906 French.
-
Niemann-Pick type C disease: NPC1 mutations associated with severe and mild cellular cholesterol trafficking alterations.Hum Genet. 2001 Jul;109(1):24-32. doi: 10.1007/s004390100531. Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11479732
-
Cause of death in patients with chronic visceral and chronic neurovisceral acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (Niemann-Pick disease type B and B variant): Literature review and report of new cases.Mol Genet Metab. 2016 Jul;118(3):206-213. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2016.05.001. Epub 2016 May 11. Mol Genet Metab. 2016. PMID: 27198631 Review.
-
The adult form of Niemann-Pick disease type C.Brain. 2007 Jan;130(Pt 1):120-33. doi: 10.1093/brain/awl260. Epub 2006 Sep 26. Brain. 2007. PMID: 17003072 Review.
Cited by
-
Challenges in the Definitive Diagnosis of Niemann-Pick Type C-Leaky Variants and Alternative Transcripts.Genes (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;14(11):1990. doi: 10.3390/genes14111990. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization of systemic AAV9 gene therapy in Niemann-Pick disease type C1 mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 8:2024.06.07.597901. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.07.597901. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38895471 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
GA4GH Phenopacket-Driven Characterization of Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Mendelian Disorders.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 6:2025.03.05.25323315. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.05.25323315. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40093222 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Membralin Selects Foreign Glycoproteins from the Endoplasmic Reticulum to Lysosomes for Degradation.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 23:rs.3.rs-6498082. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6498082/v1. Res Sq. 2025. PMID: 40678220 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Expanding what we know about rare genetic diseases.Eur J Hum Genet. 2023 Oct;31(10):1091-1092. doi: 10.1038/s41431-023-01453-2. Eur J Hum Genet. 2023. PMID: 37783763 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Patterson M. Niemann-Pick disease type C. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al. editors. GeneReviews((R)). Seattle, WA: University of Washington; 1993. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

