Early hyperbaric oxygen therapy is associated with favorable outcome in patients with iatrogenic cerebral arterial gas embolism: systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of observational studies
- PMID: 37434172
- PMCID: PMC10337083
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-023-04563-x
Early hyperbaric oxygen therapy is associated with favorable outcome in patients with iatrogenic cerebral arterial gas embolism: systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of observational studies
Abstract
Background: Iatrogenic cerebral arterial gas embolism (CAGE) caused by invasive medical procedures may be treated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT). Previous studies suggested that initiation of HBOT within 6-8 h is associated with higher probability of favorable outcome, when compared to time-to-HBOT beyond 8 h. We performed a group level and individual patient level meta-analysis of observational studies, to evaluate the relationship between time-to-HBOT and outcome after iatrogenic CAGE.
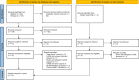
Methods: We systematically searched for studies reporting on time-to-HBOT and outcome in patients with iatrogenic CAGE. On group level, we meta-analyzed the differences between median time-to-HBOT in patients with favorable versus unfavorable outcome. On individual patient level, we analyzed the relationship between time-to-HBOT and probability of favorable outcome in a generalized linear mixed effects model.
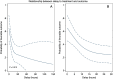
Results: Group level meta-analysis (ten studies, 263 patients) shows that patients with favorable outcome were treated with HBOT 2.4 h (95% CI 0.6-9.7) earlier than patients with unfavorable outcome. The generalized linear mixed effects model (eight studies, 126 patients) shows a significant relationship between time-to-HBOT and probability of favorable outcome (p = 0.013) that remains significant after correcting for severity of manifestations (p = 0.041). Probability of favorable outcome decreases from approximately 65% when HBOT is started immediately, to 30% when HBOT is delayed for 15 h.
Conclusions: Increased time-to-HBOT is associated with decreased probability of favorable outcome in iatrogenic CAGE. This suggests that early initiation of HBOT in iatrogenic CAGE is of vital importance.
Keywords: Air embolism; Embolic stroke; Hyperbaric oxygenation; Iatrogenic disease.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Iatrogenic cerebral gas embolism: analysis of the presentation, management and outcomes of patients referred to The Alfred Hospital Hyperbaric Unit.Diving Hyperb Med. 2016 Mar;46(1):15-21. Diving Hyperb Med. 2016. PMID: 27044457
-
Factors associated with favorable response to hyperbaric oxygen therapy among patients presenting with iatrogenic cerebral arterial gas embolism.Neurocrit Care. 2013 Apr;18(2):228-33. doi: 10.1007/s12028-012-9683-3. Neurocrit Care. 2013. PMID: 22396189
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for iatrogenic arterial gas embolism after CT-guided lung biopsy : A case report.Anaesthesist. 2019 Jul;68(7):456-460. doi: 10.1007/s00101-019-0618-7. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Anaesthesist. 2019. PMID: 31264050 English.
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for post-stroke depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020 Aug;195:105910. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105910. Epub 2020 May 16. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32474256
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and the eye.Undersea Hyperb Med. 2008 Sep-Oct;35(5):333-87. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2008. PMID: 19024664 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of hyperbaric oxygenation therapy (HBOT) on renal function in human.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 11;15(1):25143. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10569-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40646131 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral air embolism after accidental air injection into a radial artery sheath.Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2025 Apr;40(2):429-431. doi: 10.1007/s12928-025-01097-7. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2025. PMID: 39881059 No abstract available.
-
Cerebral air embolism following a hemodialysis session successfully treated with hyperbaric oxygen: a case report.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2024 Oct 9;17:17562864241287457. doi: 10.1177/17562864241287457. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2024. PMID: 39399101 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral air embolism in pediatric patients undergoing cardiac surgery.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024 Dec 19;19(1):655. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-03152-5. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 39702304 Free PMC article.
-
Decompression illness: a comprehensive overview.Diving Hyperb Med. 2024 Mar 31;54(1Suppl):1-53. doi: 10.28920/dhm54.1.suppl.1-53. Diving Hyperb Med. 2024. PMID: 38537300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brooks GJ. Pulmonary barotrauma in submarine escape trainees and the treatment of cerebral arterial air embolism. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1986;57:1201–1207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

