Internal Orifice Alloy Closure: A New Procedure for Treatment of Perianal Fistulizing Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 37434329
- PMCID: PMC10351326
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.940873
Internal Orifice Alloy Closure: A New Procedure for Treatment of Perianal Fistulizing Crohn's Disease
Abstract
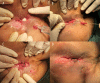
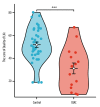
BACKGROUND The high recurrence rate of perianal fistula Crohn's disease (PFCD) increases the need to protect the anal sphincter during each surgical treatment of fistulas. We aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of internal orifice alloy closure in patients with PFCD. MATERIAL AND METHODS Fifteen patients with PFCD were enrolled in the study between July 6, 2021, and April 27, 2023. All patients underwent preoperative colonoscopy and anal magnetic resonance examination for diagnosis and evaluation. Internal orifice alloy closure (IOAC) was performed only when Crohn's disease was in remission. The external sphincter had not been severed. Perianal magnetic resonance imaging examination was used for postoperative evaluation after 6 months. Fistula cure rate, length of stay, perianal pain, and Wexner incontinence score were retrospectively compared between 15 patients treated with IOAC and 40 patients treated with other surgical methods. RESULTS Fifteen patients (male/female: 9/6, age: 23.6±14.3 years) with PFCD were included (follow-up: 24 months). In total, 20.0% (3) had multiple tracts, and 13.3% (2) had a high anal fistula. Among them, 10 patients received biologics for induction for mucosal healing before surgery. The fistula healed completely in 80.0% (12/15) and did not heal in 20.0% (3/15). Three patients who did not heal underwent fistulotomy and eventually recovered. IOAC is not superior in terms of fistula healing rates, length of stay, and anal pain, but its Wexner incontinence scores are significantly lower than with other surgical methods. CONCLUSIONS IOAC is a novel sphincter-saving surgery that is effective and safe for the treatment of PFCD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Long-term outcomes of fistula-tract laser closure for complex perianal fistulizing Crohn's disease.Tech Coloproctol. 2024 Jul 31;28(1):89. doi: 10.1007/s10151-024-02949-9. Tech Coloproctol. 2024. PMID: 39085710
-
Internal Orifice Alloy Closure-A New Procedure to Treat Anal Fistula.Front Surg. 2022 May 17;9:881060. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.881060. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 35662830 Free PMC article.
-
Total fistula volume predicts surgical outcomes in complex perianal fistulizing Crohn's disease following fistula-tract laser closure: a single-center retrospective study.Tech Coloproctol. 2025 Feb 17;29(1):70. doi: 10.1007/s10151-024-03094-z. Tech Coloproctol. 2025. PMID: 39961900 Free PMC article.
-
[Perianal Crohn's disease].Ther Umsch. 2013 Jul;70(7):417-28. doi: 10.1024/0040-5930/a000427. Ther Umsch. 2013. PMID: 23798025 Review. German.
-
Current practice and innovations in diagnosing perianal fistulizing Crohn's disease (pfCD): a narrative review.Tech Coloproctol. 2025 Apr 15;29(1):102. doi: 10.1007/s10151-025-03122-6. Tech Coloproctol. 2025. PMID: 40232330 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of neutrophil extracellular traps in Crohn's disease.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 20;10(23):e40577. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40577. eCollection 2024 Dec 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39654789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of long non-coding RNA in Crohn's disease.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 6;10(11):e32606. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32606. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38961978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the mechanical properties and clinical application of nickel-titanium shape memory alloy anal fistula clip.Front Surg. 2023 Aug 23;10:1235666. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1235666. eCollection 2023. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 37680263 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes of fistula-tract laser closure for complex perianal fistulizing Crohn's disease.Tech Coloproctol. 2024 Jul 31;28(1):89. doi: 10.1007/s10151-024-02949-9. Tech Coloproctol. 2024. PMID: 39085710
References
-
- Le Berre C, Ananthakrishnan AN, Danese S, et al. Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease have similar burden and goals for treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(1):14–23. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Chen J, Bolinger AA, et al. Target-based small molecule drug discovery towards novel therapeutics for inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27(Suppl 2):S38–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

