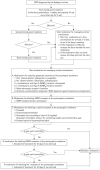
Algorithm for multimodal medication therapy in patients with complex regional pain syndrome
- PMID: 37434359
- PMCID: PMC10718613
- DOI: 10.12701/jyms.2023.00360
Algorithm for multimodal medication therapy in patients with complex regional pain syndrome
Abstract
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), previously known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy and causalgia, is a clinical entity characterized by classic neuropathic pain, autonomic involvement, motor symptoms, and trophic changes in the skin, nails, and hair. Although various therapeutic modalities are used to control CRPS-related pain, severe pain due to CRPS often persists and progresses to the chronic phase. In this study, we constructed an algorithm for multimodal medication therapy for CRPS based on the established pathology of CRPS. Oral steroid pulse therapy is recommended for initial pain management in patients with CRPS. Oral steroid therapy can reduce peripheral and central neuroinflammation, contributing to the development of neuropathic pain during the acute and chronic phases. If steroid pulse therapy offers poor relief or is ineffective, treatment to control central sensitization in the chronic phase should be initiated. If pain persists despite all drug adjustments, ketamine with midazolam 2 mg before and after ketamine injection can be administered intravenously to inhibit the N-methyl D-aspartate receptor. If this treatment fails to achieve sufficient efficacy, intravenous lidocaine can be administered for 2 weeks. We hope that our proposed drug treatment algorithm to control CRPS pain will help clinicians appropriately treat patients with CRPS. Further clinical studies assessing patients with CRPS are warranted to establish this treatment algorithm in clinical practice.
Keywords: Complex regional pain syndromes; Multimodal; Neuropathic pain; Reflex sympathetic dystrophy.
Conflict of interest statement
Min Cheol Chang has been Associate Editor of
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experience from a single-center study on multimodal medication therapy for patients with complex regional pain syndrome.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2024;37(3):687-696. doi: 10.3233/BMR-230179. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38160336
-
Anesthetic Management of a Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) Patient With Ketamine.Anesth Prog. 2020 Dec 1;67(4):219-225. doi: 10.2344/anpr-67-02-07. Anesth Prog. 2020. PMID: 33393601 Free PMC article.
-
Lidocaine infusion for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: Case series and literature review.Open Med (Wars). 2024 Dec 3;19(1):20241102. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-1102. eCollection 2024. Open Med (Wars). 2024. PMID: 39655052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Complex regional pain syndrome type I (CRPS I). Pathophysiology, diagnostics, and therapy].Orthopade. 2003 May;32(5):418-31. doi: 10.1007/s00132-003-0468-4. Orthopade. 2003. PMID: 12743694 Review. German.
-
A Novel Compound Analgesic Cream (Ketamine, Pentoxifylline, Clonidine, DMSO) for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Patients.Pain Pract. 2016 Jan;16(1):E14-20. doi: 10.1111/papr.12404. Epub 2015 Nov 7. Pain Pract. 2016. PMID: 26547813
References
-
- Kingery WS. A critical review of controlled clinical trials for peripheral neuropathic pain and complex regional pain syndromes. Pain. 1997;73:123–39. - PubMed
-
- Park GY, Park JH, Lee B, Im S, Min JH. Comparison of short-term effect between bisphosphonate and steroid therapy in hemiplegic patients with CRPS type I. J Korean Acad Rehab Med. 2009;33:103–7.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources