Psoriasis Associated Hub Genes Revealed by Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis
- PMID: 37434459
- PMCID: PMC10331440
- DOI: 10.22074/cellj.2023.1982769.1191
Psoriasis Associated Hub Genes Revealed by Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis
Abstract
Objective: Psoriasis, an immune-mediated disorder, is a multifactorial disease with unidentified cause(s). This study aimed to discover possible biomarkers of this papulosquamous skin disease.
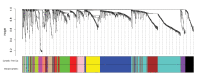
Materials and methods: The gene chip GSE55201, resulted from an experimental study, including 44 Psoriasis patients and 30 healthy controls was downloaded from GEO and weighted gene co-expression network analysis was utilized to identify hub genes. Key modules were determined using the module eigenvalues. We used biological functions (BFs), cellular components, and molecular functions in the Gene Ontology (GO) analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis in the gene metabolic pathway were used for enrichment analysis.
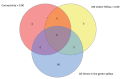
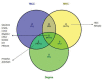
Results: Adjacency matrix was built by using power adjacency function and the power to turn the correlation to adjacency matrix was four with a topology fit index of 0.92. Using the weighted gene co-expression network analysis, 11 modules were identified. The green-yellow module eigenvalues were significantly associated with Psoriasis (Pearson correlation=0.53, P<0.001). Candidate hub genes were determined by their higher connectivity and relationship with module eigenvalue. The genes including SIGLEC8, IL5RA, CCR3, RNASE2, CPA3, GATA2, c-KIT, and PRSS33 were recorded as the hub genes.
Conclusion: We can conclude that SIGLEC8, IL5RA, CCR3, RNASE2, CPA3, GATA2, c-KIT, and PRSS33 have an important role in the immune response regulation and they could be considered as a potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for Psoriasis.
Keywords: Gene; Gene Modules; Gene Network; Psoriasis.
Figures
References
-
- Stern RS, Nijsten T, Feldman SR, Margolis DJ, Rolstad T. Psoriasis is common, carries a substantial burden even when not extensive, and is associated with widespread treatment dissatisfaction. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2004;9(2):136–139. - PubMed
-
- Javitz HS, Ward MM, Farber E, Nail L, Vallow SG. The direct cost of care for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(6):850–860. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
