Mimicking effects of cholesterol in lipid bilayer membranes by self-assembled amphiphilic block copolymers
- PMID: 37434554
- PMCID: PMC11239197
- DOI: 10.1039/d3sm00804e
Mimicking effects of cholesterol in lipid bilayer membranes by self-assembled amphiphilic block copolymers
Abstract
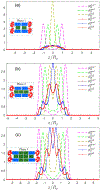
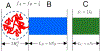
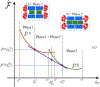
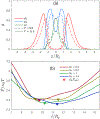
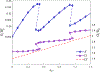
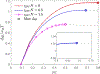
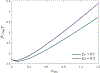
The effect of cholesterol on biological membranes is important in biochemistry. In this study, a polymer system is used to simulate the consequences of varying cholesterol content in membranes. The system consists of an AB-diblock copolymer, a hydrophilic homopolymer hA, and a hydrophobic rigid homopolymer C, corresponding to phospholipid, water, and cholesterol, respectively. The effect of the C-polymer content on the membrane is studied within the framework of a self-consistent field model. The results show that the liquid-crystal behavior of B and C has a great influence on the chemical potential of cholesterol in bilayer membranes. The effects of the interaction strength between components, characterized by the Flory-Huggins parameters and the Maier-Saupe parameter, were studied. Some consequences of adding a coil headgroup to the C-rod are presented. Results of our model are compared to experimental findings for cholesterol-containing lipid bilayer membranes.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

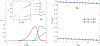







Similar articles
-
Cholesterol Content Regulates the Interaction of αA-, αB-, and α-Crystallin with the Model of Human Lens-Lipid Membranes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 5;25(3):1923. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031923. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339200 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Cholesterol on the Insertion and Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 Proteins with Lipid Membranes.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025 Jun 16;8(6):5380-5394. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.5c00776. Epub 2025 Jun 6. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025. PMID: 40474679 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of amphiphilic carbosilane dendrons on lipid model membranes.Chem Phys Lipids. 2023 Sep;255:105314. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2023.105314. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Chem Phys Lipids. 2023. PMID: 37356611
-
Cationic Proteins Rich in Lysine Residue Trigger Formation of Non-bilayer Lipid Phases in Model and Biological Membranes: Biophysical Methods of Study.J Membr Biol. 2023 Dec;256(4-6):373-391. doi: 10.1007/s00232-023-00292-y. Epub 2023 Sep 21. J Membr Biol. 2023. PMID: 37735238 Review.
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Phillips R, Kondev J, Theriot J and Garcia H, Physical biology of the cell, Garland Science, 2012.
-
- Singer SJ and Nicolson GL, Science, 1972, 175, 720–731. - PubMed
-
- Deleu M, Crowet J-M, Nasir MN and Lins L, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes, 2014, 1838, 3171–3190. - PubMed
-
- Lange Y, Journal of lipid research, 1991, 32, 329–339. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

