Research on orchard navigation method based on fusion of 3D SLAM and point cloud positioning
- PMID: 37434606
- PMCID: PMC10330707
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1207742
Research on orchard navigation method based on fusion of 3D SLAM and point cloud positioning
Abstract
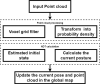
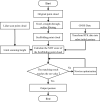
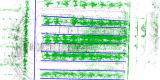
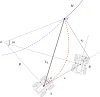
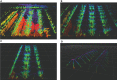
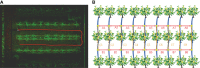
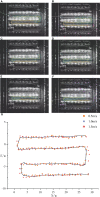
Accurate navigation is crucial in the construction of intelligent orchards, and the need for vehicle navigation accuracy becomes even more important as production is refined. However, traditional navigation methods based on global navigation satellite system (GNSS) and 2D light detection and ranging (LiDAR) can be unreliable in complex scenarios with little sensory information due to tree canopy occlusion. To solve these issues, this paper proposes a 3D LiDAR-based navigation method for trellis orchards. With the use of 3D LiDAR with a 3D simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm, orchard point cloud information is collected and filtered using the Point Cloud Library (PCL) to extract trellis point clouds as matching targets. In terms of positioning, the real-time position is determined through a reliable method of fusing multiple sensors for positioning, which involves transforming the real-time kinematics (RTK) information into the initial position and doing a normal distribution transformation between the current frame point cloud and the scaffold reference point cloud to match the point cloud position. For path planning, the required vector map is manually planned in the orchard point cloud to specify the path of the roadway, and finally, navigation is achieved through pure path tracking. Field tests have shown that the accuracy of the normal distributions transform (NDT) SLAM method can reach 5 cm in each rank with a coefficient of variation that is less than 2%. Additionally, the navigation system has a high positioning heading accuracy with a deviation within 1° and a standard deviation of less than 0.6° when moving along the path point cloud at a speed of 1.0 m/s in a Y-trellis pear orchard. The lateral positioning deviation was also controlled within 5 cm with a standard deviation of less than 2 cm. This navigation system has a high level of accuracy and can be customized to specific tasks, making it widely applicable in trellis orchards with autonomous navigation pesticide sprayers.
Keywords: LiDAR; SLAM; autonomous navigation; orchard; robot; vector map.
Copyright © 2023 Xia, Lei, Pan, Chen, Zhang and Lyu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Bakker T., Van Asselt K., Bontsema J., Müller J., Van Straten G. (2011). Autonomous navigation using a robot platform in a sugar beet field. Biosyst. Eng. 109, 357–368. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2011.05.001 - DOI
-
- Bayar G., Bergerman M., Koku A. B., Ilhan Konukseven E. (2015). Localization and control of an autonomous orchard vehicle. Comput. Electron. Agric. 115, 118–128. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2015.05.015 - DOI
-
- Biber P., Straßer W. (2003). “The normal distributions transform: a new approach to laser scan matching,” in Proceedings2002, 003 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS2002, 003)(Cat. no. 03CH37453) (IEEE; ), 3, 2743–2748. doi: 10.1109/IROS.2003.1249285 - DOI
-
- Bin X., Junxiong Z., Feng Q., Zhiqi F., Dashuai W., Wei L. (2017). Navigation control system for orchard spraying machine based on beidou navigation satellite system. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Transact. Chin. Soc. Agric. Machinery 48, 45–50. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2017.02.006 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

