Preoperative low-density lipoprotein cholesterol as a predictor of favorable prognosis in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 37434674
- PMCID: PMC10331453
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-22-2705
Preoperative low-density lipoprotein cholesterol as a predictor of favorable prognosis in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Studies have shown that dyslipidemia is closely tied to a variety of cancers, and the level of low-density-lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) is related to the prognosis of cancer patients. However, what remains unclear is the predictive meaning of LDL-C among patients who suffer from renal cell carcinoma, especially clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC). The aim of this study was to investigate the correlation between the preoperative levels of serum LDL-C and the prognosis of surgical patients who suffer from clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Methods: A total of 308 CCRCC patients that received radical or partial nephrectomy were retrospectively included in this study. The clinical data of each included patient were collected. Overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) were calculated using Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazards regression model.
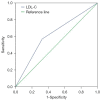
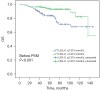
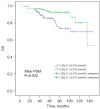
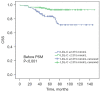
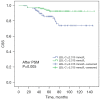
Results: Univariate analysis showed that a higher LDL-C level indicated a better OS and CSS in CCRCC patients (P=0.002 and P=0.001, respectively). The same was shown in the Multivariate analysis that a higher LDL-C level indicated a better OS and CSS in CCRCC patients (P<0.001 and P<0.001, respectively). Following propensity score matching (PSM) analysis, a higher LDL-C level still existed as an ideal indicator for both OS and CSS.
Conclusions: The study indicated that a higher serum level of LDL-C showed clinical significance for predicting better OS and CSS in patients with CCRCC.
Keywords: Low-density-lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C); clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC); operation; prognosis.
2023 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-22-2705/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preoperative serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is an independent prognostic factor in patients with renal cell carcinoma after nephrectomy.Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Feb 22;22(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01791-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 36814277 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol as a predictor of poor survival in patients with clear cell renal cell cancer.Int J Biol Markers. 2019 Jun;34(2):168-175. doi: 10.1177/1724600819831404. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Int J Biol Markers. 2019. PMID: 30912469
-
[Correlation between metabolic syndrome and prognosis of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Aug 18;54(4):636-643. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.04.009. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 35950385 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Does chromophobe renal cell carcinoma have better survival than clear cell renal cell carcinoma? A clinical-based cohort study and meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2016 Feb;48(2):191-9. doi: 10.1007/s11255-015-1161-3. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26589610 Review.
-
A new CCCH-type zinc finger-related lncRNA signature predicts the prognosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 30;13:1034567. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1034567. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36246657 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Blood lipid metabolic biomarkers are emerging as significant prognostic indicators for survival in cancer patients.BMC Cancer. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):1549. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13265-8. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39695484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prochazkova K, Ptakova N, Alaghehbandan R, et al. Mutation Profile Variability in the Primary Tumor and Multiple Pulmonary Metastases of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. A Review of the Literature and Analysis of Four Metastatic Cases. Cancers (Basel) 2021;13:5906. 10.3390/cancers13235906 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
