Fluorescence microscopy-based sensitive method to quantify dopaminergic neurodegeneration in a Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 37434762
- PMCID: PMC10332464
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1158858
Fluorescence microscopy-based sensitive method to quantify dopaminergic neurodegeneration in a Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
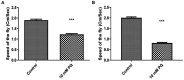
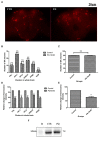
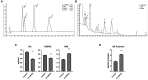
Death of dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the human brain is the characteristic pathological feature of Parkinson's disease (PD). On exposure to neurotoxicants, Drosophila too exhibits mobility defects and diminished levels of brain dopamine. In the fly model of sporadic PD, our laboratory has demonstrated that there is no loss of DAergic neuronal number, however, a significant reduction in fluorescence intensity (FI) of secondary antibodies that target the primary antibody-anti-tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). Here, we present a sensitive, economical, and repeatable assay to characterize neurodegeneration based on the quantification of FI of the secondary antibody. As the intensity of fluorescence correlates with the amount of TH synthesis, its reduction under PD conditions denotes the depletion in the TH synthesis, suggesting DAergic neuronal dysfunction. Reduction in TH protein synthesis is further confirmed through Bio-Rad Stain-Free Western Blotting. Quantification of brain DA and its metabolites (DOPAC and HVA) using HPLC-ECD further demonstrated the depleted DA level and altered DA metabolism as evident from enhanced DA turnover rate. Together all these PD marker studies suggest that FI quantification is a refined and sensitive method to understand the early stages of DAergic neurodegeneration. FI quantification is performed using ZEN 2012 SP2, a licensed software from Carl Zeiss, Germany. This method will be of good use to biologists, as it with few modifications, can also be implemented to characterize the extent of degeneration of different cell types. Unlike the expensive and cumbersome confocal microscopy, the present method using fluorescence microscopy will be a feasible option for fund-constrained neurobiology laboratories in developing countries.
Keywords: Drosophila; dopamine; fluorescence intensity; neurodegeneration; tyrosine hydroxylase.
Copyright © 2023 Ayajuddin, Chaurasia, Das, Modi, Phom, Koza and Yenisetti.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Simple Immunofluorescence Method to Characterize Neurodegeneration and Tyrosine Hydroxylase Reduction in Whole Brain of a Drosophila Model of Parkinson's Disease.Bio Protoc. 2024 Feb 20;14(4):e4937. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4937. eCollection 2024 Feb 20. Bio Protoc. 2024. PMID: 38405079 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual dysfunction precedes motor defects, dopaminergic neuronal degeneration, and impaired dopamine metabolism: Insights from Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease.Front Neurosci. 2023 Mar 21;17:1143793. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1143793. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37025374 Free PMC article.
-
Adult health and transition stage-specific rotenone-mediated Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease: Impact on late-onset neurodegenerative disease models.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Aug 9;15:896183. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.896183. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36017079 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic targeting of histone deacetylase: therapeutic potential in Parkinson's disease?Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Oct;140(1):34-52. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.05.010. Epub 2013 May 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23711791 Review.
-
Impact of Dopamine Oxidation on Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019 Feb 20;10(2):945-953. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00454. Epub 2019 Jan 17. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30592597 Review.
Cited by
-
A Simple Immunofluorescence Method to Characterize Neurodegeneration and Tyrosine Hydroxylase Reduction in Whole Brain of a Drosophila Model of Parkinson's Disease.Bio Protoc. 2024 Feb 20;14(4):e4937. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4937. eCollection 2024 Feb 20. Bio Protoc. 2024. PMID: 38405079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayajuddin M., Das A., Phom L., Koza Z., Chaurasia R., Yenisetti S. C. (2021). “Quantification of dopamine and its metabolites in Drosophila brain using HPLC” in Experiments with Drosophila for biology courses. eds. Lakhotia S. C., Ranganath H. A. (Bengaluru: Indian Academy of Sciences; ), 433–440.
-
- Ayajuddin M., Phom L., Koza Z., Modi P., Das A., Chaurasia R., et al. . (2022). Adult health and transition stage-specific rotenone mediated Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease: impact on late-onset neurodegenerative disease models. Front Mol Neurosci. 15:896183. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.896183, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

