Renal Replacement Therapy For Elderly Patients with ESKD Through Shared Decision-Making
- PMID: 37434803
- PMCID: PMC10329902
- DOI: 10.5049/EBP.2023.21.1.1
Renal Replacement Therapy For Elderly Patients with ESKD Through Shared Decision-Making
Abstract
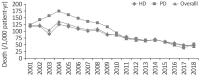
The incidence and prevalence of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) in Korea are increasing, and ESKD constitutes a very important medical and social issue. Elderly dialysis patients have the highest risk of early mortality within 3 months after initiating dialysis, and geriatric syndromes such as aging, frailty, functional impairment, and cognitive impairment are crucial for the prognosis of elderly patients. Shared decision-making (SDM) is an approach through which clinicians and patients can achieve informed preferences, thereby yielding better clinical outcomes and quality of life. Through SDM-based, close consultation among patients, families, and healthcare providers, an ESKD Life-Plan for elderly patients should be established. A multidisciplinary approach led by nephrologists can help them to provide proper vascular access for dialysis at the right time, with the right evidence, and to the right patient. Strategies that can improve peritoneal dialysis in elderly patients include assisted peritoneal dialysis, homecare support programs, and automated peritoneal dialysis. In order to enhance the role of kidney transplantation in elderly patients with ESKD, it is necessary to accurately identify patients' clinical conditions before transplantation and to perform active rehabilitation activities and postoperative management to promote recovery after transplantation. With the aging population and the increase in ESKD in the elderly, clinicians must identify factors affecting the mortality and quality of life of elderly dialysis patients.
Keywords: Elderly; End-Stage Kidney Disease Life-Plan; Hemodialysis; Kidney transplantation; Peritoneal dialysis; Renal replacement therapy; Shared decision making.
Copyright © 2023 Korean Society for Electrolyte and Blood Pressure Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[The Veneto Region's Registry of Dialysis and Transplantation: 2006-2007 report].G Ital Nefrol. 2009 Nov-Dec;26 Suppl 48:S5-56. G Ital Nefrol. 2009. PMID: 19927265 Italian.
-
Renal replacement therapy in geriatric end-stage renal disease patients: a clinical approach.Blood Purif. 2012;33(1-3):171-6. doi: 10.1159/000334153. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Blood Purif. 2012. PMID: 22269680 Review.
-
Assisted peritoneal dialysis as a method of choice for elderly with end-stage renal disease.Int Urol Nephrol. 2008;40(4):1143-50. doi: 10.1007/s11255-008-9427-7. Epub 2008 Jul 23. Int Urol Nephrol. 2008. PMID: 18649003 Review.
-
Survival advantage of initiating dialysis in elderly and non-elderly incident end-stage kidney disease patients.Nephrology (Carlton). 2020 Aug;25(8):644-651. doi: 10.1111/nep.13689. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Nephrology (Carlton). 2020. PMID: 31900988
-
Incorporating Patients' Values and Preferences Into Decision Making About Transplantation of HCV-Naïve Recipients With Kidneys From HCV-Viremic Donors: A Feasibility Study.MDM Policy Pract. 2021 Oct 29;6(2):23814683211056537. doi: 10.1177/23814683211056537. eCollection 2021 Jul-Dec. MDM Policy Pract. 2021. PMID: 34734119 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dialysis nurse demand in Europe: an estimated prediction based on modelling.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Jun 3;17(7):sfae162. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae162. eCollection 2024 Jul. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 38974818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 2020 Annual Data Report, USRDS.
-
- Jassal SV, Watson D. Dialysis in late life: benefit or burden. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(12):2008–2012. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
