Defeating Melanoma Through a Nano-Enabled Revision of Hypoxic and Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 37435153
- PMCID: PMC10332423
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S414882
Defeating Melanoma Through a Nano-Enabled Revision of Hypoxic and Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
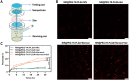
Rationale: Reversing the hypoxic and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) is crucial for treating malignant melanoma. Seeking a robust platform for the effective reversion of hypoxic and immunosuppressive TME may be an excellent solution to revolutionizing the current landscape of malignant melanoma treatment. Here, we demonstrated a transdermal and intravenous dual-administration paradigm. A tailor-made Ato/cabo@PEG-TK-PLGA NPs were administrated transdermally to melanoma with the help of a gel spray containing a skin-penetrating material borneol. Nanoparticles encased Ato and cabo were released and thereby reversed the hypoxic and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME).
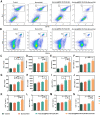
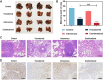
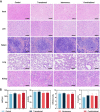
Methods: Ato/cabo@PEG-TK-PLGA NPs were synthesized through a self-assembly emulsion process, and the transdermal ability was assessed using Franz diffusion cell assembly. The inhibition effect on cell respiration was measured by OCR, ATP, and pO2 detection and in vivo photoacoustic (PA) imaging. The reversing of the immunosuppressive was detected through flow cytometry analysis of MDSCs and T cells. At last, the in vivo anti-tumor efficacy and histopathology, immunohistochemical analysis and safety detection were performed using tumor-bearing mice.
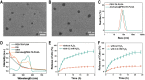
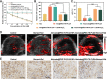
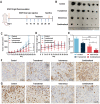
Results: The transdermally administrated Ato/cabo@PEG-TK-PLGA NPs successfully spread to the skin surface of melanoma and then entered deep inside the tumor with the help of a gel spray and a skin puncturing material borneol. Atovaquone (Ato, a mitochondrial-respiration inhibitor) and cabozantinib (cabo, a MDSCs eliminator) were concurrently released in response to the intratumorally overexpressed H2O2. The released Ato and cabo respectively reversed the hypoxic and immunosuppressive TME. The reversed hypoxic TME offered sufficient O2 for the intravenously administrated indocyanine green (ICG, an FDA-approved photosensitizer) to produce adequate amount of ROS. In contrast, the reversed immunosuppressive TME conferred amplified systemic immune responses.
Conclusion: Taken together, we developed a transdermal and intravenous dual-administration paradigm, which effectively reversed the hypoxic and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in the treatment of the malignant melanoma. We believe our study will open a new path for the effective elimination of the primary tumors and the real-time control of tumor metastasis.
Keywords: hypoxia; immunosuppression; melanoma; transdermal administration; tumor microenvironment.
© 2023 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Atovaquone-HSA nano-drugs enhance the efficacy of PD-1 blockade immunotherapy by alleviating hypoxic tumor microenvironment.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Oct 2;19(1):302. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01034-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34600560 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor microenvironment remodeling and tumor therapy based on M2-like tumor associated macrophage-targeting nano-complexes.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(6):2892-2916. doi: 10.7150/thno.50928. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33456579 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor microenvironment-responsive nanozymes achieve photothermal-enhanced multiple catalysis against tumor hypoxia.Acta Biomater. 2021 Nov;135:617-627. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.08.015. Epub 2021 Aug 15. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 34407474
-
The application of nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapy: Targeting tumor microenvironment.Bioact Mater. 2020 Dec 26;6(7):1973-1987. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.12.010. eCollection 2021 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 33426371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting anticancer immunity in melanoma tumour microenvironment: unleashing the potential of adjuvants, drugs, and phytochemicals.J Drug Target. 2024 Nov;32(9):1052-1072. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2024.2384071. Epub 2024 Aug 7. J Drug Target. 2024. PMID: 39041142 Review.
Cited by
-
Phase-Inversion In Situ Systems: Problems and Prospects of Biomedical Application.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jun 6;17(6):750. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060750. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40574062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in mechanisms and challenges in clinical translation of synergistic nanomaterial-based therapies for melanoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jul 25;13:1648379. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1648379. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40787624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

