Outcome analysis in patients with metastatic gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors receiving peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with Lu-177-DOTATATE
- PMID: 37435198
- PMCID: PMC10331769
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-22-874
Outcome analysis in patients with metastatic gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors receiving peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with Lu-177-DOTATATE
Abstract
Background: Patients with neuroendocrine tumors (NET) of the gastroenteropancreatic tract (GEP-NET) were effectively treated with peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) with Lu-177-DOTATATE in the NETTER-1 trial. The aim of this study was to assess the outcome of metastatic GEP-NET patients within a European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society (ENETS) certified center of excellence after this treatment.
Methods: A total of 41 GEP-NET patients who received PRRT with Lu-177-DOTATATE between 2012 and 2017 at a single center were included in this analysis. Data on pre- and post-PRRT treatments [selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT), somatostatin analogue therapy (SSA), blood parameters, patient symptomatic burden and overall survival] was extracted from patient records.
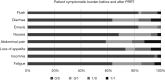
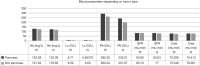
Results: Overall, PRRT was well tolerated and did not increase patient symptomatic burden. Blood parameters were not significantly affected by PRRT (means before and after therapy: hemoglobin: 125.4 vs. 122.3 mg/L, P=0.201; creatinine: 73.8 vs. 77.7 µmol/L, P=0.146), while leukocytes (6.6 vs. 5.6 G/L, P<0.01) and platelets (269.9 vs. 216.7 G/L, P<0.001) were significantly decreased yet without clinical significance in our study. Seven of 9 patients with SIRT treatment prior to PRRT were deceased (mortality odds ratio =4.083). The mortality odds ratio of patients with a pancreatic tumor and SIRT was 1.33 compared to patients with a different tumor origin. 6 of 15 patients (40%) with post-PRRT SSA were deceased (mortality odds ratio =0.429 without SSA after PRRT).
Conclusions: Patients with advanced GEP-NET might benefit from PRRT with Lu-177-DOTATATE as it can provide a valuable treatment modality in advanced disease stages. Safety profiles of PRRT were manageable without increasing the symptomatic burden. SIRT before PRRT or lack of SSA after PRRT seem to impair the response and reduce survival.
Keywords: Lu-177-DOTATATE; Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT); health-related quality of life (HRQoL); mortality; neuroendocrine tumors (NET); selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT); somatostatin analogue therapy (SSA).
2023 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-22-874/coif). ARS has served at advisory boards and received consulting honoraria from AMGEN, AAA, Bayer, BMS, IPSEN, Lilly, Merck, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, and Servier, and has received travel grants from IPSEN and ROCHE, outside the submitted work. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Survival Outcomes in Metastatic Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Patients receiving Concomitant 225Ac-DOTATATE Targeted Alpha Therapy and Capecitabine: A Real-world Scenario Management Based Long-term Outcome Study.J Nucl Med. 2022 Jul 21:jnumed.122.264043. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.122.264043. Online ahead of print. J Nucl Med. 2022. PMID: 35863893
-
Initial clinical evaluation of indigenous 90Y-DOTATATE in sequential duo-PRRT approach (177Lu-DOTATATE and 90Y-DOTATATE) in neuroendocrine tumors with large bulky disease: Observation on tolerability, 90Y-DOTATATE post- PRRT imaging characteristics (bremsstrahlung and PETCT) and early adverse effects.World J Nucl Med. 2020 Oct 2;20(1):73-81. doi: 10.4103/wjnm.WJNM_52_20. eCollection 2021 Jan-Mar. World J Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 33850492 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Hematotoxicity of PRRT with Lutathera® and Locally Manufactured 177Lu-HA-DOTATATE in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors and the Impact of Different Application Intervals.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 24;17(9):1423. doi: 10.3390/cancers17091423. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361351 Free PMC article.
-
A Clinical Guide to Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy with 177Lu-DOTATATE in Neuroendocrine Tumor Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 24;14(23):5792. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235792. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy for Advanced Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors - from oncology perspective.Nucl Med Rev Cent East Eur. 2018;21(2). doi: 10.5603/NMR.2018.0019. Nucl Med Rev Cent East Eur. 2018. PMID: 29741203 Review.
References
-
- Pelosi G, Volante M, Papotti M, et al. Peptide receptors in neuroendocrine tumors of the lung as potential tools for radionuclide diagnosis and therapy. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2006;50:272-87. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
