AKR1C1 overexpression leads to lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37435231
- PMCID: PMC10331763
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-23-277
AKR1C1 overexpression leads to lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Lenvatinib is an orally administered drug that works as a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor. It has been approved as a first-line drug after sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, little is currently known about its treatment, targets, and possible resistance in HCC.
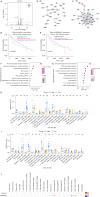
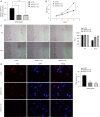
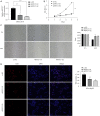
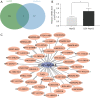
Methods: The proliferation of HCC cells was evaluated using colony formation, 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EDU), wound healing, cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), and xenograft tumor assays. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was utilized to comprehensively examine variations in highly metastatic human liver cancer cells (MHCC-97H) cells (treated with various doses of lenvatinib) at the transcriptomic level. Protein interactions and functions were predicted using Cytoscape-generated networks and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment, while the proportions of 22 immune cell types were examined with CIBERSORT. Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C1 (AKR1C1) expression was verified by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) or immunohistochemistry in HCC cells and liver tissues. Micro ribonucleic acid (miRNAs) were predicted using online tools and potential drugs were screened using the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC) database.
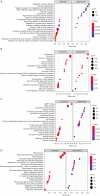
Results: Lenvatinib inhibited the proliferation of HCC cells. The obtained results suggested that an elevated level of AKR1C1 expression was observed in lenvatinib-resistant (LR) cell lines and HCC tissues, whereas low AKR1C1 expression inhibited the proliferation of HCC cells. Circulating microRNA 4644 (miR-4644) was predicted to serve as a promising biomarker for the early diagnosis of lenvatinib resistance. Online data analysis of LR cells showed significant differences in the immune microenvironment and drug sensitivity compared with their parental counterparts.
Conclusions: Taken together, AKR1C1 may serve as a candidate therapeutic target for LR liver cancer patients.
Keywords: Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C1 (AKR1C1); biomarker; drug sensitivity; hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); lenvatinib resistance.
2023 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-23-277/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




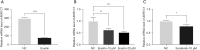

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-128-3p Mediates Lenvatinib Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Downregulating c-Met.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022 Feb 27;9:113-126. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S349369. eCollection 2022. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022. PMID: 35252056 Free PMC article.
-
Sophoridine suppresses lenvatinib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma growth by inhibiting RAS/MEK/ERK axis via decreasing VEGFR2 expression.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jan;25(1):549-560. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16108. Epub 2020 Nov 18. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33210432 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of the lncRNA HOTAIRM1 promotes lenvatinib resistance by downregulating miR-34a and activating autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2023 May 12;14(1):66. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00673-8. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37171645 Free PMC article.
-
Lenvatinib as a therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2018 Nov;18(11):1069-1076. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2018.1524297. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2018. PMID: 30220234 Review.
-
Lenvatinib: established and promising drug for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Nov;14(11):1353-1365. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2021.1958674. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34289756 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of clinical application of lenvatinib and its resistance mechanism in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (Review).Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 15;14(9):4113-4171. doi: 10.62347/UJVP4361. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39417171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-22 signaling promotes sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via STAT3/CD155 signaling axis.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 25;15:1373321. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1373321. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38596684 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the potential function of high expression of ANAPC1 in regulating ubiquitination in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 May 15;17(5):103594. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.103594. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40487972 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating T-cell inflammation features for prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: a novel predictive model.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Dec 31;15(6):2613-2629. doi: 10.21037/jgo-2024-874. Epub 2024 Dec 28. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39816015 Free PMC article.
-
ALG3 as a prognostic biomarker and mediator of PD-1 blockade resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2025 May 22;16:1589153. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1589153. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40475760 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
