How Not To Fix a Tibial Fracture: A Case Report on Treatment By a Quack
- PMID: 37435249
- PMCID: PMC10331172
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.40203
How Not To Fix a Tibial Fracture: A Case Report on Treatment By a Quack
Abstract
Quackery in the orthopaedic profession has existed for quite a long time. Due to the shortage of orthopaedic healthcare staff in public hospitals and the high costs in private facilities, members of disadvantaged communities turn to unlicensed and unskilled practitioners (quacks). The main factors responsible for the increased number of quacks performing orthopaedic treatment are illiteracy, high treatment cost, mismatch in the orthopaedic surgeon-to-population ratio, especially in rural areas, and the absence of any form of health insurance. Moreover, their easy availability and offer of low-cost treatment draw innocent and illiterate patients to them, even though these quacks perform orthopaedic treatment in the most unhygienic, unsterilized, and unconventional manner. The government should intervene and take measures to make orthopaedic treatment more affordable and accessible, especially to the rural population.
Keywords: infections; mismanagement; non-union; quack; tbs (traditional bone setter).
Copyright © 2023, Singh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
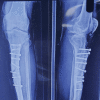
Figures



References
-
- Evaluation of problems related to malpractice and professionalism in Islamabad area-a study. Khan AS, Syed AY, Qureshi AM, Ijaz SH, Khan AA. https://pesquisa.bvsalud.org/portal/resource/pt/emr-174418 Pak Oral Dental J. 2004;24:74–76.
-
- Performance of a trained traditional bonesetter in primary fracture care. Onuminya JE. https://journals.co.za/doi/abs/10.10520/EJC68703. South African Medical Journal. 20061;96:320–322. - PubMed
-
- Complications of fracture treatment by traditional bonesetters in southwest Nigeria. OlaOlorun DA, Oladiran IO, Adeniran A. Fam Pract. 2001;18:635–637. - PubMed
-
- Treatment by quacks still an issue of concern. Zameer A, Vakil SM, Bhat TA, Dhar SA, Khurshid L, Sofi AH. https://www.longdom.org/open-access/treatment-by-quacks-still-an-issue-o... Orthop Muscular Syst. 2016;5:120.
-
- The strengths and weaknesses of Turkish bone-setters. Hatipoğlu S, Tatar K. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7794467/ World Health Forum. 1995;16:203–205. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
