Oxidative stress, DNA damage, and inflammation in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 37435296
- PMCID: PMC10331251
- DOI: 10.14744/nci.2022.00947
Oxidative stress, DNA damage, and inflammation in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Objective: Severe inflammation and oxidative stress seen in COVID-19 patients cause cumulative antiviral effects, and serious inflammation increases tissue, oxidative damage, and DNA damage. Therefore, in this study, oxidative stress, DNA damage, and inflammation biomarkers were investigated in patients diagnosed with COVID-19.
Methods: In this study, blood samples were obtained from 150 Covid-19 patients diagnosed by polymerase chain reaction and 150 healthy volunteers with the same demographic characteristics. Total oxidant status (TOS), total antioxidant status (TAS), total thiol (TT), native thiol, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activities were measured by photometric methods. The levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), and interleukin 6 (IL-6), which are inflammation markers, were measured by the ELISA method using commercial kits. The genotoxic effect was evaluated by Comet Assay.
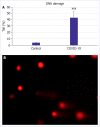
Results: The oxidative stress biomarkers; Disulfide, TOS, MPO, oxidative stress index, and IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels of inflammation biomarkers and the DNA damage in COVID-19 patients were increased (p<0.001), and the levels of TAS, TT, and NT In COVID-19 patients were decreased (p<0.001).
Conclusion: In COVID-19 patients, induced DNA damage, inflammation, and oxidative stress can guide the prognosis and treatment strategies of the disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; genotoxicity; oxidative stress.
© Copyright 2023 by Istanbul Provincial Directorate of Health.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Lov DK, Alkhovsky SV. Source of the COVID-19 pandemic: ecology and genetics of coronaviruses (Betacoronavirus: Coronaviridae) SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 (subgenus Sarbecovirus), and MERS-CoV (subgenus Merbecovirus) Vopr Virusol. 2020;65:62–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
