Research on equity of medical resource allocation in Yangtze River Economic Belt under healthy China strategy
- PMID: 37435525
- PMCID: PMC10332165
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1175276
Research on equity of medical resource allocation in Yangtze River Economic Belt under healthy China strategy
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess the fairness of medical resource allocation in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, based on the Healthy China strategy. It aimed to identify the issues with resource allocation fairness and provide optimization suggestions.
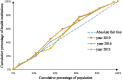
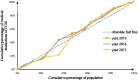
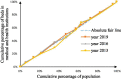
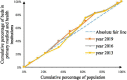
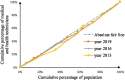
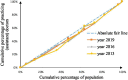
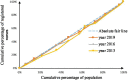
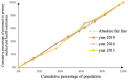
Methods: To assess the allocation fairness from a geographical population perspective, the study used the Health Resource Concentration and Entropy Weight TOPSIS methods. Additionally, the study analyzed the allocation fairness from an economic level angle, using the Concentration Curve and Concentration Index.
Results: The study found that the downstream area had higher resource allocation fairness than the midstream and upstream areas. The middle reaches had more resources than the upper and lower reaches, based on population concentration. The Entropy Weight TOPSIS method found that Shanghai, Zhejiang, Chongqing, and Jiangsu had the highest comprehensive score index of agglomeration. Furthermore, from 2013 to 2019, the fairness of medical resource distribution gradually improved for different economic levels. Government health expenditure and medical beds were distributed more equitably, while general practitioners had the highest level of unfairness. However, except for medical and health institutions, traditional Chinese medicine institutions, and primary health institutions, other medical resources were mostly distributed to areas with better economic conditions.
Conclusion: The study found that the fairness of medical resource allocation in the Yangtze River Economic Belt varied greatly based on geographical population distribution, with inadequate spatial accessibility and service accessibility. Although the fairness of distribution based on economic levels improved over time, medical resources were still concentrated in better economic areas. The study recommends improving regional coordinated development to enhance the fairness of medical resource allocation in the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
Keywords: Yangtze River Economic Belt; data envelopment analysis; equality; health equalities; healthy China strategy.
Copyright © 2023 Ya-qing, Hao-ran, Xiang-yang, Mei-cheng, Feng, Yu-tong and Jian-bo.
Conflict of interest statement
TX-y was employed by China State Construction Silkroad Construction Investment Group co., LTD. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen Lei H, Lijun HF. Research on the impact of the development strategy of the Yangtze River Economic Belt on regional economic ties -- an empirical test based on the double difference method. Econ Longitude Latitude. (2021) 38:23–32. doi: 10.15931/j.cnki.1006-1096.20210210.002 - DOI
-
- Qi W. The Outline of the Yangtze River Economic Belt development plan was officially issued half a month (2016) 18:91.
-
- Zhao Z, Juan L. The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the state council issued the outline of the “healthy China 2030”. Plan Bulletin of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China (2016) 32:5–20.
-
- Anonymous, The 14th Five-Year Plan . For the National Economic and social development of the People’s Republic of China and the outline of the vision and objectives for 2035. Xinhua Monthly News People’s Daily (2021) 69, 79–126.
-
- Yizhou H. Fairness and supply-demand relationship prediction of medical and health resources allocation in Shanwei City. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University; (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

