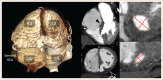
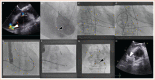
Percutaneous Transcatheter Closure of Post-infarction Ventricular Septal Defect: An Alternative to Surgical Intervention
- PMID: 37435604
- PMCID: PMC10331564
- DOI: 10.15420/icr.2023.01
Percutaneous Transcatheter Closure of Post-infarction Ventricular Septal Defect: An Alternative to Surgical Intervention
Abstract
Post-infarction ventricular septal defect is a mechanical complication of acute MI. The incidence of this complication is low in the primary percutaneous coronary intervention era. However, the associated mortality is very high at 94% with medical management alone. Open surgical repair or percutaneous transcatheter closure still has an in-hospital mortality >40%. Retrospective comparisons between both closure methods are limited by observation and selection bias. This review addresses the assessment and optimisation of patients prior to repair, the optimal timing of repair, and the limitations in current data. The review considers techniques for percutaneous closure, and finally considers the path that future research should take to improve outcomes for patients.
Keywords: Post-infarction ventricular septal defect; acute MI; percutaneous closure of ventricular septal defect; ventricular septal rupture.
Copyright © 2023, Radcliffe Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: LKW has received speaker fees from Medtronic Europe. PAC has acted as a proctor for Abbott Vascular. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Cooley DA, Belmonte BA, Zeis LB, Schnur S. Surgical repair of ruptured interventricular septum following acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 1957;41:930–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources