Effects of sevoflurane on metalloproteinase and natural killer group 2, member D (NKG2D) ligand expression and natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity in breast cancer: an in vitro study
- PMID: 37435613
- PMCID: PMC10718625
- DOI: 10.4097/kja.23323
Effects of sevoflurane on metalloproteinase and natural killer group 2, member D (NKG2D) ligand expression and natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity in breast cancer: an in vitro study
Abstract
Background: We investigated the effects of sevoflurane exposure on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), expression and ablation of natural killer group 2, member D (NKG2D) ligands (UL16-binding proteins 1-3 and major histocompatibility complex class I chain-related molecules A/B), and natural killer (NK) cell-mediated cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells.
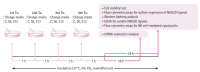
Methods: Three human breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7, MDA-MB-453, and HCC-70) were incubated with 0 (control), 600 (S6), or 1200 μM (S12) sevoflurane for 4 h. The gene expression of NKG2D ligands and their protein expression on cancer cell surfaces were measured using multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and flow cytometry, respectively. Protein expression of MMP-1 and -2 and the concentration of soluble NKG2D ligands were analyzed using western blotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, respectively.
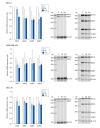
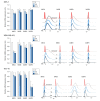
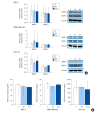
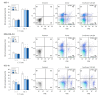
Results: Sevoflurane downregulated the mRNA and protein expression of the NKG2D ligand in a dose-dependent manner in MCF-7, MDA-MB-453, and HCC-70 cells but did not affect the expression of MMP-1 or -2 or the concentration of soluble NKG2D ligands in the MCF-7, MDA-MB-453, and HCC-70 cells. Sevoflurane attenuated NK cell-mediated cancer cell lysis in a dose-dependent manner in MCF-7, MDA-MB-453, and HCC-70 cells (P = 0.040, P = 0.040, and P = 0.040, respectively).
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that sevoflurane exposure attenuates NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner. This could be attributed to a sevoflurane-induced decrease in the transcription of NKG2D ligands rather than sevoflurane-induced changes in MMP expression and their proteolytic activity.
Keywords: Breast neoplasms; Inhalation anesthetics; Matrix metalloproteinases; Natural killer cells; Sevoflurane; Tumor escape..
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Receptor subtype-dependent effects of propofol on metalloproteinase activity, NKG2D ligand expression, and NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity in breast cancer: an in vitro study.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2025 May 7. doi: 10.4097/kja.25011. Online ahead of print. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40754850
-
Role of Sevoflurane on Natural Killer Group 2, Member D-Mediated Immune Response in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An In Vitro Study.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Nov 3;26:e926395. doi: 10.12659/MSM.926395. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 33139690 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of MMP activity can restore NKG2D ligand expression in gastric cancer, leading to improved NK cell susceptibility.J Gastroenterol. 2016 Dec;51(12):1101-1111. doi: 10.1007/s00535-016-1197-x. Epub 2016 Mar 22. J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27002316
-
Generation of soluble NKG2D ligands: proteolytic cleavage, exosome secretion and functional implications.Scand J Immunol. 2013 Aug;78(2):120-9. doi: 10.1111/sji.12072. Scand J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23679194 Review.
-
Role of Polymorphisms of NKG2D Receptor and Its Ligands in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Human Stem Cell Transplantation.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 30;12:651751. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.651751. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NKG2D (Natural Killer Group 2, Member D) ligand expression and ameloblastoma recurrence: a retrospective immunohistological pilot study.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Sep 17;24(1):1102. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04873-8. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39289711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carrière G, Sanmartin C, Murison P. Using data linkage to report surgical treatment of breast cancer in Canada. Health Rep. 2018;29:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Merchant N, Nagaraju GP, Rajitha B, Lammata S, Jella KK, Buchwald ZS, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases: their functional role in lung cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2017;38:766–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

