Pre-existing T Cell Memory to Novel Pathogens
- PMID: 37436166
- PMCID: PMC10587503
- DOI: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2200003
Pre-existing T Cell Memory to Novel Pathogens
Abstract
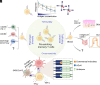
Immunological experiences lead to the development of specific T and B cell memory, which readies the host for a later pathogen rechallenge. Currently, immunological memory is best understood as a linear process whereby memory responses are generated by and directed against the same pathogen. However, numerous studies have identified memory cells that target pathogens in unexposed individuals. How "pre-existing memory" forms and impacts the outcome of infection remains unclear. In this review, we discuss differences in the composition of baseline T cell repertoire in mice and humans, factors that influence pre-existing immune states, and recent literature on their functional significance. We summarize current knowledge on the roles of pre-existing T cells in homeostasis and perturbation and their impacts on health and disease.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Flaxman, S., Whittaker C., Semenova E., Rashid T., Parks R. M., Blenkinsop A., Unwin H. J. T., Mishra S., Bhatt S., Gurdasani D., Ratmann O.. 2023. Assessment of COVID-19 as the underlying cause of death among children and young people aged 0 to 19 Years in the US. JAMA Netw. Open 6: e2253590. - PMC - PubMed
-
- El-Sadr, W. M., Vasan A., El-Mohandes A.. 2023. Facing the new Covid-19 reality. N. Engl. J. Med. 388: 385–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

