Sedation with a 1:1 mixture of etomidate and propofol for gastroscopy in hypertensive elderly patients
- PMID: 37436589
- PMCID: PMC10423762
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.14693
Sedation with a 1:1 mixture of etomidate and propofol for gastroscopy in hypertensive elderly patients
Abstract
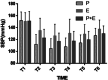
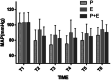
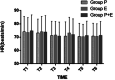
We hypothesized that the combined use of etomidate and propofol for endoscopic sedation in elderly hypertensive patients could reduce adverse reactions while providing ideal sedation. To validate our hypothesis, we conducted a prospective, randomized, controlled, double-blinded study. A total of 360 elderly hypertensive patients scheduled for gastroscopy at our hospital were enrolled in the study, of whom 328 completed the trial. The patients were randomly assigned to one of three groups: the propofol group (group P), the etomidate group (group E), or the propofol-etomidate combination group (mixed at a ratio of 1:1, group PE). We collected and analyzed the cardiopulmonary effects and side effects in each group. Regardless of the sedation drug used, the systolic blood pressure, mean blood pressure, and heart rate of involved patients were significantly affected. Oxygen desaturation and injection pain were more common in group P compared to groups E (33.6% vs. 14.8%, 31.8% vs. 2.7%, both P < 0.01) and group PE (33.6% vs. 13.6%, 31.8% vs. 6.4%, both P < 0.01). The incidence of myoclonus in the PE group was lower than that in the E group (10.9% vs. 61.2%, P < 0.01). Our results indeed demonstrated that the combined use of etomidate and propofol appeared to maintain cardiopulmonary stability with minimal side effects in older hypertensive patients scheduled for gastroscopy, which further implied that this sedation strategy could be a safe and pain-free option for managing patients undergoing gastroscopy, particularly those at a higher risk of adverse cardiovascular events.
Keywords: elderly; etomidate; gastroscopy; hypertension; propofol; sedation.
© 2023 The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of ciprofol, propofol, and propofol and etomidate mixture, and ciprofol and etomidate mixture in patients undergoing painless gastroscopy: A randomized, double-blind controlled clinical trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Sep 6;103(36):e39585. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039585. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39252308 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of combined use of propofol and etomidate for sedation during gastroscopy: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 May;98(20):e15712. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015712. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31096522 Free PMC article.
-
Etomidate-remifentanil is more suitable for monitored anesthesia care during gastroscopy in older patients than propofol-remifentanil.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Jan 1;21:1-8. doi: 10.12659/MSM.891183. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 25553506 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical observation of the combined use of propofol and etomidate in painless gastroscopy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 6;99(45):e23061. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023061. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33157963 Free PMC article.
-
Etomidate versus propofol for sedation in gastrointestinal endoscopy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Feb 10;102(6):e32876. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032876. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36820568 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The 50% effective dose of remimazolam combined with different doses of esketamine for painless gastroscopy.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 14;15(1):12770. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97649-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40229355 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of different doses of alfentanil on cardiovascular response to rapid sequence intubation in elderly patients: a parallel-controlled randomized trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Aug 13;24(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02663-x. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39138407 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Application of dexmedetomidine combined with propofol-etomidate mixture in radical gastrectomy under general anesthesia.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 1;103(44):e39669. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039669. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39496064 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ye L, Xiao X, Zhu L. The comparison of etomidate and propofol anesthesia in patients undergoing gastrointestinal endoscopy: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2017;27(1):1‐7. - PubMed
-
- Kim MG, Park SW, Kim JH, et al. Etomidate versus propofol sedation for complex upper endoscopic procedures: a prospective double‐blinded randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86(3):452‐461. - PubMed
-
- Doenicke AW, RM Kugler J, Kroll H, et al. Reducing myoclonus after etomidate. Anesthesiology. 1999;90(1):113‐119. - PubMed
-
- Peacock JE, Lewis RP, Reilly CS, et al. Effect of different rates of infusion of propofol for induction of anaesthesia in elderly patients. Br J Anaesth. 1990;65(3):346‐352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

