Cost-effectiveness analysis of 7 treatments in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer: a public-payer perspective
- PMID: 37436697
- PMCID: PMC10637034
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djad135
Cost-effectiveness analysis of 7 treatments in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer: a public-payer perspective
Abstract
Background: Recently, several new treatment regimens have been approved for treating metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, building on androgen deprivation therapy alone. These include docetaxel androgen deprivation therapy, abiraterone acetate-prednisone androgen deprivation therapy, apalutamide androgen deprivation therapy, enzalutamide androgen deprivation therapy, darolutamide-docetaxel androgen deprivation therapy, and abiraterone-prednisone androgen deprivation therapy with docetaxel. There are no validated predictive biomarkers for choosing a specific regimen. The goal of this study was to conduct a health economic outcome evaluation to determine the optimal treatment from the US public sector (Veterans Affairs).
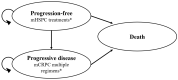
Methods: We developed a partitioned survival model in which metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer patients transitioned between 3 health states (progression free, progressive disease to castrate resistance state, and death) at monthly intervals based on Weibull survival model estimated from published Kaplan-Meier curves using a Bayesian network meta-analysis of 7 clinical trials (7208 patients). The effectiveness outcome in our model was quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). Cost input parameters included initial and subsequent treatment costs and costs for terminal care and for managing grade 3 or higher drug-related adverse events and were obtained from the Federal Supply Schedule and published literature.
Results: Average 10-year costs ranged from $34 349 (androgen deprivation therapy) to $658 928 (darolutamide-docetaxel androgen deprivation therapy) and mean QALYs ranged from 3.25 (androgen deprivation therapy) to 4.57 (enzalutamide androgen deprivation therapy). Treatment strategies docetaxel androgen deprivation therapy, enzalutamide androgen deprivation therapy docetaxel, apalutamide androgen deprivation therapy, and darolutamide-docetaxel androgen deprivation therapy were eliminated because of dominance (ie, they were more costly and less effective than other strategies). Of the remaining strategies, abiraterone acetate-prednisone androgen deprivation therapy was the most cost-effective strategy at a willingness-to-pay threshold of $100 000/QALY (incremental cost-effectiveness ratios = $21 247/QALY).
Conclusions: Our simulation model found abiraterone acetate-prednisone androgen deprivation therapy to be an optimal first-line treatment for metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer from a public (Veterans Affairs) payer perspective.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A.. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA A Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(1):7-33. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. - PubMed
-
- Fizazi K, Tran N, Fein L, et al. ; for the LATITUDE Investigators. Abiraterone plus prednisone in metastatic, castration-sensitive prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(4):352-360. - PubMed
-
- Fizazi K, Tran N, Fein L, et al. Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone in patients with newly diagnosed high-risk metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (LATITUDE): final overall survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(5):686-700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

