Novel SOX10 indel mutations drive schwannomas through impaired transactivation of myelination gene programs
- PMID: 37436963
- PMCID: PMC10708934
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noad121
Novel SOX10 indel mutations drive schwannomas through impaired transactivation of myelination gene programs
Abstract
Background: Schwannomas are common peripheral nerve sheath tumors that can cause severe morbidity given their stereotypic intracranial and paraspinal locations. Similar to many solid tumors, schwannomas and other nerve sheath tumors are primarily thought to arise due to aberrant hyperactivation of the RAS growth factor signaling pathway. Here, we sought to further define the molecular pathogenesis of schwannomas.
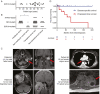
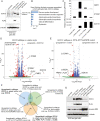
Methods: We performed comprehensive genomic profiling on a cohort of 96 human schwannomas, as well as DNA methylation profiling on a subset. Functional studies including RNA sequencing, chromatin immunoprecipitation-DNA sequencing, electrophoretic mobility shift assay, and luciferase reporter assays were performed in a fetal glial cell model following transduction with wildtype and tumor-derived mutant isoforms of SOX10.
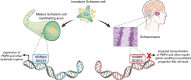
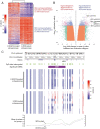
Results: We identified that nearly one-third of sporadic schwannomas lack alterations in known nerve sheath tumor genes and instead harbor novel recurrent in-frame insertion/deletion mutations in SOX10, which encodes a transcription factor responsible for controlling Schwann cell differentiation and myelination. SOX10 indel mutations were highly enriched in schwannomas arising from nonvestibular cranial nerves (eg facial, trigeminal, vagus) and were absent from vestibular nerve schwannomas driven by NF2 mutation. Functional studies revealed these SOX10 indel mutations have retained DNA binding capacity but impaired transactivation of glial differentiation and myelination gene programs.
Conclusions: We thus speculate that SOX10 indel mutations drive a unique subtype of schwannomas by impeding proper differentiation of immature Schwann cells.
Keywords: PMP2; SOX10; Schwann cell; myelination; schwannoma.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
E.A.W., D.A.M., R.S.P.H., M.C.H., D.C.P., G.M.F., T.J., and J.S.R. are employees/consultants of Foundation Medicine, Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Roche Holdings, Inc. and Roche Finance Ltd, and these employees have equity interest in an affiliate of these Roche entities. S.M.C., M.S.B., and J.F.C. are editorial board members of
Figures


Comment in
-
Unraveling schwannomas.Neuro Oncol. 2023 Dec 8;25(12):2237-2238. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noad171. Neuro Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37715980 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Trofatter JA, MacCollin MM, Rutter JL, et al. . A novel moesin-, ezrin-, radixin-like gene is a candidate for the neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor. Cell. 1993;72(5):791–800. - PubMed
-
- Sestini R, Bacci C, Provenzano A, Genuardi M, Papi L.. Evidence of a four-hit mechanism involving SMARCB1 and NF2 in schwannomatosis-associated schwannomas. Hum Mutat. 2008;29(2):227–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

