The secreted neuronal signal Spock1 promotes blood-brain barrier development
- PMID: 37437574
- PMCID: PMC10525910
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2023.06.005
The secreted neuronal signal Spock1 promotes blood-brain barrier development
Abstract
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a unique set of properties of the brain vasculature which severely restrict its permeability to proteins and small molecules. Classic chick-quail chimera studies have shown that these properties are not intrinsic to the brain vasculature but rather are induced by surrounding neural tissue. Here, we identify Spock1 as a candidate neuronal signal for regulating BBB permeability in zebrafish and mice. Mosaic genetic analysis shows that neuronally expressed Spock1 is cell non-autonomously required for a functional BBB. Leakage in spock1 mutants is associated with altered extracellular matrix (ECM), increased endothelial transcytosis, and altered pericyte-endothelial interactions. Furthermore, a single dose of recombinant SPOCK1 partially restores BBB function in spock1 mutants by quenching gelatinase activity and restoring vascular expression of BBB genes including mcamb. These analyses support a model in which neuronally secreted Spock1 initiates BBB properties by altering the ECM, thereby regulating pericyte-endothelial interactions and downstream vascular gene expression.
Keywords: blood vessel; blood-brain barrier; development; genetics; leakage; zebrafish.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
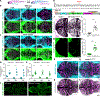
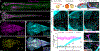
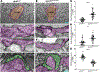




References
-
- Andreone BJ, Chow BW, Tata A, Lacoste B, Ben-Zvi A, Bullock K, Deik AA, Ginty DD, Clish CB, and Gu C (2017). Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability Is Regulated by Lipid Transport-Dependent Suppression of Caveolae-Mediated Transcytosis. Neuron 94, 581–594.e5. 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.03.043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

