Microbiologically influenced corrosion-more than just microorganisms
- PMID: 37437902
- PMCID: PMC10479746
- DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuad041
Microbiologically influenced corrosion-more than just microorganisms
Abstract
Microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) is a phenomenon of increasing concern that affects various materials and sectors of society. MIC describes the effects, often negative, that a material can experience due to the presence of microorganisms. Unfortunately, although several research groups and industrial actors worldwide have already addressed MIC, discussions are fragmented, while information sharing and willingness to reach out to other disciplines are limited. A truly interdisciplinary approach, which would be logical for this material/biology/chemistry-related challenge, is rarely taken. In this review, we highlight critical non-biological aspects of MIC that can sometimes be overlooked by microbiologists working on MIC but are highly relevant for an overall understanding of this phenomenon. Here, we identify gaps, methods, and approaches to help solve MIC-related challenges, with an emphasis on the MIC of metals. We also discuss the application of existing tools and approaches for managing MIC and propose ideas to promote an improved understanding of MIC. Furthermore, we highlight areas where the insights and expertise of microbiologists are needed to help progress this field.
Keywords: biocorrosion; biodeterioration; interdisciplinarity; microbiologically influenced corrosion; multiple lines of evidence.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
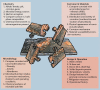

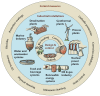


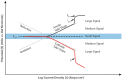
References
-
- euro-mic.org. Euro-MIC: Europen Network for MIC Management. https://www.euro-mic.org/ (13 February 2023, date last accessed).
-
- Abdolahi A, Hamzah E, Ibrahim Zet al. Application of environmentally-friendly coatings toward inhibiting the microbially influenced corrosion (MIC) of steel: a review. Polym Rev. 2014;54:702–45.
-
- Ackland BG, Dylejko KP. Critical questions and answers about cathodic protection. Corros Eng Sci Technol. 2019;54:688–97.
-
- Al Jahdaly BA, Maghraby YR, Ibrahim AHet al. Role of green chemistry in sustainable corrosion inhibition: a review on recent developments. Mater Today Sustain. 2022;20:100242.
-
- Amaya H, Miyuki H, Takeishi Yet al. Effects of shape weld bead on bacterial adhesion and MIC occurrence at stainless steel welded joints. CORROSION. 2002;2002. https://onepetro.org/NACECORR/proceedings-abstract/CORR02/All-CORR02/NAC...(Paper Number: NACE-02556 Denver, Colorado).

