Gut-microbiota in children and adolescents with obesity: inferred functional analysis and machine-learning algorithms to classify microorganisms
- PMID: 37438382
- PMCID: PMC10338520
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-36533-2
Gut-microbiota in children and adolescents with obesity: inferred functional analysis and machine-learning algorithms to classify microorganisms
Abstract
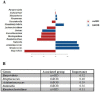
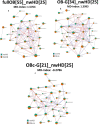
The fecal microbiome of 55 obese children and adolescents (BMI-SDS 3.2 ± 0.7) and of 25 normal-weight subjects, matched both for age and sex (BMI-SDS - 0.3 ± 1.1) was analysed. Streptococcus, Acidaminococcus, Sutterella, Prevotella, Sutterella wadsworthensis, Streptococcus thermophilus, and Prevotella copri positively correlated with obesity. The inferred pathways strongly associated with obesity concern the biosynthesis pathways of tyrosine, phenylalanine, tryptophan and methionine pathways. Furthermore, polyamine biosynthesis virulence factors and pro-inflammatory lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis pathway showed higher abundances in obese samples, while the butanediol biosynthesis showed low abundance in obese subjects. Different taxa strongly linked with obesity have been related to an increased risk of multiple diseases involving metabolic pathways related to inflammation (polyamine and lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis). Cholesterol, LDL, and CRP positively correlated with specific clusters of microbial in obese patients. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes-ratio was lower in obese samples than in controls and differently from the literature we state that this ratio could not be a biomarker for obesity.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

