A framework for individualized splice-switching oligonucleotide therapy
- PMID: 37438524
- PMCID: PMC10371869
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06277-0
A framework for individualized splice-switching oligonucleotide therapy
Abstract
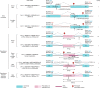
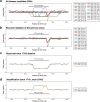
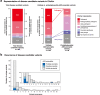
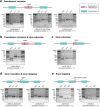
Splice-switching antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) could be used to treat a subset of individuals with genetic diseases1, but the systematic identification of such individuals remains a challenge. Here we performed whole-genome sequencing analyses to characterize genetic variation in 235 individuals (from 209 families) with ataxia-telangiectasia, a severely debilitating and life-threatening recessive genetic disorder2,3, yielding a complete molecular diagnosis in almost all individuals. We developed a predictive taxonomy to assess the amenability of each individual to splice-switching ASO intervention; 9% and 6% of the individuals had variants that were 'probably' or 'possibly' amenable to ASO splice modulation, respectively. Most amenable variants were in deep intronic regions that are inaccessible to exon-targeted sequencing. We developed ASOs that successfully rescued mis-splicing and ATM cellular signalling in patient fibroblasts for two recurrent variants. In a pilot clinical study, one of these ASOs was used to treat a child who had been diagnosed with ataxia-telangiectasia soon after birth, and showed good tolerability without serious adverse events for three years. Our study provides a framework for the prospective identification of individuals with genetic diseases who might benefit from a therapeutic approach involving splice-switching ASOs.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.K. and T.W.Y. are listed as inventors on pending patent claims (US 62/912,997) filed by Boston Children’s Hospital covering
Figures












Comment in
-
Creating a path to splice-switching ASO therapies.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023 Sep;22(9):693. doi: 10.1038/d41573-023-00124-7. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023. PMID: 37528209 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

