Mast cells link immune sensing to antigen-avoidance behaviour
- PMID: 37438525
- PMCID: PMC10432277
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06188-0
Mast cells link immune sensing to antigen-avoidance behaviour
Abstract
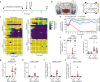
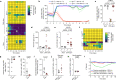
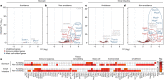
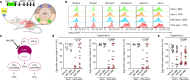
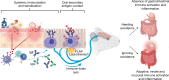
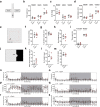
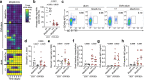
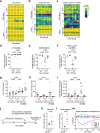
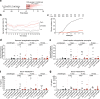
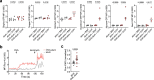
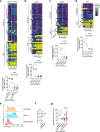
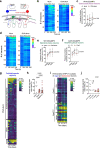
The physiological functions of mast cells remain largely an enigma. In the context of barrier damage, mast cells are integrated in type 2 immunity and, together with immunoglobulin E (IgE), promote allergic diseases. Allergic symptoms may, however, facilitate expulsion of allergens, toxins and parasites and trigger future antigen avoidance1-3. Here, we show that antigen-specific avoidance behaviour in inbred mice4,5 is critically dependent on mast cells; hence, we identify the immunological sensor cell linking antigen recognition to avoidance behaviour. Avoidance prevented antigen-driven adaptive, innate and mucosal immune activation and inflammation in the stomach and small intestine. Avoidance was IgE dependent, promoted by Th2 cytokines in the immunization phase and by IgE in the execution phase. Mucosal mast cells lining the stomach and small intestine rapidly sensed antigen ingestion. We interrogated potential signalling routes between mast cells and the brain using mutant mice, pharmacological inhibition, neural activity recordings and vagotomy. Inhibition of leukotriene synthesis impaired avoidance, but overall no single pathway interruption completely abrogated avoidance, indicating complex regulation. Collectively, the stage for antigen avoidance is set when adaptive immunity equips mast cells with IgE as a telltale of past immune responses. On subsequent antigen ingestion, mast cells signal termination of antigen intake. Prevention of immunopathology-causing, continuous and futile responses against per se innocuous antigens or of repeated ingestion of toxins through mast-cell-mediated antigen-avoidance behaviour may be an important arm of immunity.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
The immunology that underlies picky eating.Nature. 2023 Aug;620(7974):497-499. doi: 10.1038/d41586-023-02179-3. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37438630 No abstract available.
-
To eat or not to eat: type 2 immunity controls food avoidance behavior.Trends Immunol. 2023 Sep;44(9):665-667. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2023.07.007. Epub 2023 Aug 15. Trends Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37586904
-
Making good of a tricky start: How IgE and mast cells manage a protective sway in food allergy.Immunity. 2023 Sep 12;56(9):1988-1990. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.08.010. Immunity. 2023. PMID: 37703829
References
-
- Cara DC, Conde AA, Vaz NM. Immunological induction of flavor aversion in mice. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1994;27:1331–1341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

