High-throughput Oligopaint screen identifies druggable 3D genome regulators
- PMID: 37438531
- PMCID: PMC11305015
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06340-w
High-throughput Oligopaint screen identifies druggable 3D genome regulators
Abstract
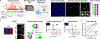
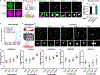
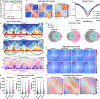
The human genome functions as a three-dimensional chromatin polymer, driven by a complex collection of chromosome interactions1-3. Although the molecular rules governing these interactions are being quickly elucidated, relatively few proteins regulating this process have been identified. Here, to address this gap, we developed high-throughput DNA or RNA labelling with optimized Oligopaints (HiDRO)-an automated imaging pipeline that enables the quantitative measurement of chromatin interactions in single cells across thousands of samples. By screening the human druggable genome, we identified more than 300 factors that influence genome folding during interphase. Among these, 43 genes were validated as either increasing or decreasing interactions between topologically associating domains. Our findings show that genetic or chemical inhibition of the ubiquitous kinase GSK3A leads to increased long-range chromatin looping interactions in a genome-wide and cohesin-dependent manner. These results demonstrate the importance of GSK3A signalling in nuclear architecture and the use of HiDRO for identifying mechanisms of spatial genome organization.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



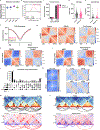
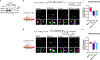
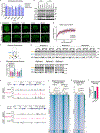

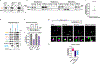


References
SUPPLEMENTARY REFERENCES
-
- Saito Y & Kanemaki MT Targeted Protein Depletion Using the Auxin-Inducible Degron 2 (AID2) System. Curr. Protoc 1, e219 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Beckwith KS et al. Visualization of loop extrusion by nanoscale 3D DNA tracing in single human cells. 2021.04.12.439407 Preprint at 10.1101/2021.04.12.439407 (2022). - DOI
-
- Cho KF et al. Proximity labeling in mammalian cells with TurboID and split-TurboID. Nat. Protoc 15, 3971–3999 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

