Hyperuricemia and gout increased the risk of long-term mortality in patients with heart failure: insights from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- PMID: 37438830
- PMCID: PMC10339518
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04307-z
Hyperuricemia and gout increased the risk of long-term mortality in patients with heart failure: insights from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of hyperuricemia, gout, and heart failure (HF) is on the rise, and these conditions often share similar risk factors. The present study aimed to evaluate the relationship among hyperuricemia, gout, HF, and all-cause mortality.
Methods: The data on nonpregnant participants aged ≥ 20 years with or without hyperuricemia, gout, and HF from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001-2018 and 2007-2018 were included in this study. The binary logistic regression, Kaplan-Meier curve, Cox proportional-hazards model, and restricted cubic spline analysis were employed to evaluate the relationship among hyperuricemia, gout, HF, and all-cause mortality.
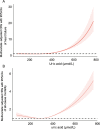
Results: Of 204,179,060 and 223,702,171 weighted eligible participants, 40,044,228 (19.6%) and 9,158,600 (4.1%) had hyperuricemia and gout, respectively. Older age, diabetes, stroke, and coronary artery disease were the risk factors for HF among patients with hyperuricemia and gout. The median survival time was 7.00 years and 6.25 years and the 5-year survival rate was 59.9% and 55.9% for patients with HF and hyperuricemia and those with HF and gout, respectively. Patients with hyperuricemia or gout were 2.46 and 2.35 times more likely to have HF and 1.37 and 1.45 times more likely to experience all-cause mortality compared with those who did not exhibit these conditions. The restricted cubic spline showed a nonlinear correlation between uric acid levels and HF and a J-shaped correlation between uric acid levels and all-cause mortality.
Conclusions: Ambulatory patients with hyperuricemia or gout were more likely to have HF compared with those without hyperuricemia or gout. Patients with HF with hyperuricemia or gout were more likely to experience all-cause mortality in the long-term follow-up.
Keywords: Gout; Heart failure; Mortality; NHANES; Uric acid.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

