An 8-channel Tx dipole and 20-channel Rx loop coil array for MRI of the cervical spinal cord at 7 Tesla
- PMID: 37439129
- PMCID: PMC10733907
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.5002
An 8-channel Tx dipole and 20-channel Rx loop coil array for MRI of the cervical spinal cord at 7 Tesla
Abstract
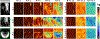
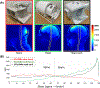
The quality of cervical spinal cord images can be improved by the use of tailored radiofrequency (RF) coil solutions for ultrahigh field imaging; however, very few commercial and research 7-T RF coils currently exist for the spinal cord, and in particular, those with parallel transmission (pTx) capabilities. This work presents the design, testing, and validation of a pTx/Rx coil for the human neck and cervical/upper thoracic spinal cord. The pTx portion is composed of eight dipoles to ensure high homogeneity over this large region of the spinal cord. The Rx portion is made up of twenty semiadaptable overlapping loops to produce high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) across the patient population. The coil housing is designed to facilitate patient positioning and comfort, while also being tight fitting to ensure high sensitivity. We demonstrate RF shimming capabilities to optimize B1 + uniformity, power efficiency, and/or specific absorption rate efficiency. B1 + homogeneity, SNR, and g-factor were evaluated in adult volunteers and demonstrated excellent performance from the occipital lobe down to the T4-T5 level. We compared the proposed coil with two state-of-the-art head and head/neck coils, confirming its superiority in the cervical and upper thoracic regions of the spinal cord. This coil solution therefore provides a convincing platform for producing the high image quality necessary for clinical and research scanning of the upper spinal cord.
Keywords: 7 T; MRI; dipole; radiofrequency coil; spinal cord; transmit/receive coil; ultrahigh field.
© 2023 The Authors. NMR in Biomedicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Update of
-
8-channel Tx dipole and 20-channel Rx loop coil array for MRI of the cervical spinal cord at 7 Tesla.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 9:2023.02.08.527664. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.08.527664. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: NMR Biomed. 2023 Nov;36(11):e5002. doi: 10.1002/nbm.5002. PMID: 36798276 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Multi-center benchmarking of cervical spinal cord RF coils for 7 T MRI: A traveling spines study.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Sep;94(3):1339-1355. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30551. Epub 2025 May 20. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 40391630 Free PMC article.
-
8-channel Tx dipole and 20-channel Rx loop coil array for MRI of the cervical spinal cord at 7 Tesla.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 9:2023.02.08.527664. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.08.527664. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: NMR Biomed. 2023 Nov;36(11):e5002. doi: 10.1002/nbm.5002. PMID: 36798276 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Flexible array coil for cervical and extraspinal (FACE) MRI at 3.0 Tesla.Phys Med Biol. 2023 Oct 26;68(21). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ad0217. Phys Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37816375
-
Translating state-of-the-art spinal cord MRI techniques to clinical use: A systematic review of clinical studies utilizing DTI, MT, MWF, MRS, and fMRI.Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Dec 4;10:192-238. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.11.019. eCollection 2016. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 26862478 Free PMC article.
-
Uncommon Non-MS Demyelinating Disorders of the Central Nervous System.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):45. doi: 10.1007/s11910-025-01432-8. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40591029 Review.
Cited by
-
Reliability of task-based fMRI in the dorsal horn of the human spinal cord.Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024 Aug 22;2:imag-2-00273. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00273. eCollection 2024. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024. PMID: 40800541 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-center benchmarking of cervical spinal cord RF coils for 7 T MRI: A traveling spines study.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Sep;94(3):1339-1355. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30551. Epub 2025 May 20. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 40391630 Free PMC article.
-
Body size and intracranial volume interact with the structure of the central nervous system: A multi-center in vivo neuroimaging study.Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025 May 7;3:imag_a_00559. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00559. eCollection 2025. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40800833 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous whole-brain and cervical spine imaging at 7 T using a neurovascular head and neck coil with 8-channel transceiver array and 56-channel receiver array.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Jul;94(1):386-400. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30450. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 39887456 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability of task-based fMRI in the dorsal horn of the human spinal cord.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 25:2023.12.22.572825. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.22.572825. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024 Aug 22;2:imag-2-00273. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00273. PMID: 38187724 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- May MW, Hansen SLJD, Kutscha N, et al. A Patient-Friendly 16ch Tx / 64ch Rx Array for Combined Head and Neck Imaging at 7 Tesla. In: ISMRM 2021 ; 2021. https://submissions2.mirasmart.com/ISMRM2021/ViewSubmission.aspx?sbmID=3...
-
- Pfaffenrot V, Brunheim S, Rietsch SHG, et al. An 8/15-channel Tx/Rx head neck RF coil combination with region-specific B1 + shimming for whole-brain MRI focused on the cerebellum at 7T. Magn Reson Med 2018;80(3):1252–1265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

