Prediction of oxygen supplementation by a deep-learning model integrating clinical parameters and chest CT images in COVID-19
- PMID: 37440160
- PMCID: PMC10687147
- DOI: 10.1007/s11604-023-01466-3
Prediction of oxygen supplementation by a deep-learning model integrating clinical parameters and chest CT images in COVID-19
Abstract
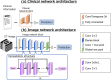
Purpose: As of March 2023, the number of patients with COVID-19 worldwide is declining, but the early diagnosis of patients requiring inpatient treatment and the appropriate allocation of limited healthcare resources remain unresolved issues. In this study we constructed a deep-learning (DL) model to predict the need for oxygen supplementation using clinical information and chest CT images of patients with COVID-19.
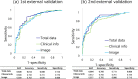
Materials and methods: We retrospectively enrolled 738 patients with COVID-19 for whom clinical information (patient background, clinical symptoms, and blood test findings) was available and chest CT imaging was performed. The initial data set was divided into 591 training and 147 evaluation data. We developed a DL model that predicted oxygen supplementation by integrating clinical information and CT images. The model was validated at two other facilities (n = 191 and n = 230). In addition, the importance of clinical information for prediction was assessed.
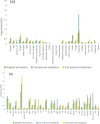
Results: The proposed DL model showed an area under the curve (AUC) of 89.9% for predicting oxygen supplementation. Validation from the two other facilities showed an AUC > 80%. With respect to interpretation of the model, the contribution of dyspnea and the lactate dehydrogenase level was higher in the model.
Conclusions: The DL model integrating clinical information and chest CT images had high predictive accuracy. DL-based prediction of disease severity might be helpful in the clinical management of patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chest CT images; Deep learning; Disease severity prediction; Explainable AI.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
3D CT-Inclusive Deep-Learning Model to Predict Mortality, ICU Admittance, and Intubation in COVID-19 Patients.J Digit Imaging. 2023 Apr;36(2):603-616. doi: 10.1007/s10278-022-00734-4. Epub 2022 Nov 30. J Digit Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36450922 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning With Chest Radiographs for Making Prognoses in Patients With COVID-19: Retrospective Cohort Study.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Feb 16;25:e42717. doi: 10.2196/42717. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 36795468 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Patient Management in COVID-19 Using Deep Learning-Based Fully Automated Extraction of Cardiothoracic CT Metrics and Laboratory Findings.Korean J Radiol. 2021 Jun;22(6):994-1004. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0994. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Korean J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33686818 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Asymptomatic COVID-19 Patients on Chest CT Images Using Transformer-Based or Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Learning Models.J Digit Imaging. 2023 Jun;36(3):827-836. doi: 10.1007/s10278-022-00754-0. Epub 2023 Jan 3. J Digit Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36596937 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the models generated from clinical features and deep learning-based segmentations: Can thoracic CT on admission help us to predict hospitalized COVID-19 patients who will require intensive care?BMC Med Imaging. 2022 Jun 7;22(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00833-2. BMC Med Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35672719 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nonrigid registration method for longitudinal chest CT images in COVID-19.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 31;10(17):e37272. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37272. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39286087 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Analysis for Lung Disease on Thin-Section CT.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Sep 18;13(18):2988. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13182988. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37761355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of short-term follow-up chest CT images using a latent diffusion model in COVID-19.Jpn J Radiol. 2025 Apr;43(4):622-633. doi: 10.1007/s11604-024-01699-w. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Jpn J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39585556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports.Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. World Health Organization; 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019. (Accessed 8 Mar 2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

