A urokinase-associated outbreak of Ralstonia mannitolilytica bloodstream infections in haemodialysis patients in north-eastern Italy, January to April 2023
- PMID: 37440346
- PMCID: PMC10347894
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2023.28.28.2300328
A urokinase-associated outbreak of Ralstonia mannitolilytica bloodstream infections in haemodialysis patients in north-eastern Italy, January to April 2023
Abstract
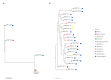
An outbreak of Ralstonia mannitolilytica bloodstream infections occurred in four hospitals in north-eastern Italy, involving 20 haemodialysis patients with tunnelled central vascular catheter access. We identified as the outbreak source a batch of urokinase vials imported from India contaminated with R. mannitolilytica. Whole genome sequences of the clinical and urokinase strains were highly related, and only urokinase-treated patients were reported with R. mannitolilytica infections (attack rate = 34%; 95% confidence interval: 22.1-47.4). Discontinuation of the contaminated urokinase terminated the outbreak.
Keywords: Outbreak; Ralstonia; bacteraemia; catheter; dialysis; mannitolilytica; sepsis; urokinase.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Di Pilato V, Henrici De Angelis L, Aiezza N, Baccani I, Niccolai C, Parisio EM, et al. . Resistome and virulome accretion in an NDM-1-producing ST147 sublineage of Klebsiella pneumoniae associated with an outbreak in Tuscany, Italy: a genotypic and phenotypic characterisation. Lancet Microbe. 2022;3(3):e224-34. 10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00268-8 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
