RHINO directs MMEJ to repair DNA breaks in mitosis
- PMID: 37440612
- PMCID: PMC10561558
- DOI: 10.1126/science.adh3694
RHINO directs MMEJ to repair DNA breaks in mitosis
Abstract
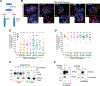
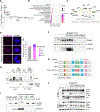
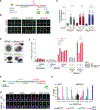
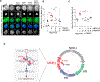
Nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR) are the primary pathways for repairing DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) during interphase, whereas microhomology-mediated end-joining (MMEJ) has been regarded as a backup mechanism. Through CRISPR-Cas9-based synthetic lethal screens in cancer cells, we identified subunits of the 9-1-1 complex (RAD9A-RAD1-HUS1) and its interacting partner, RHINO, as crucial MMEJ factors. We uncovered an unexpected function for RHINO in restricting MMEJ to mitosis. RHINO accumulates in M phase, undergoes Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) phosphorylation, and interacts with polymerase θ (Polθ), enabling its recruitment to DSBs for subsequent repair. Additionally, we provide evidence that MMEJ activity in mitosis repairs persistent DSBs that originate in S phase. Our findings offer insights into the synthetic lethal relationship between the genes POLQ and BRCA1 and BRAC2 and the synergistic effect of Polθ and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Update of
-
RHINO restricts MMEJ activity to mitosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 16:2023.03.16.532763. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.16.532763. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Science. 2023 Aug 11;381(6658):653-660. doi: 10.1126/science.adh3694. PMID: 36993461 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
RHINO and Polθ Mediate DNA Double-Strand Break Repair during Mitosis.Cancer Discov. 2023 Sep 6;13(9):OF8. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-RW2023-119. Cancer Discov. 2023. PMID: 37504678
References
-
- Schrempf A, Slyskova J, Loizou JI, Targeting the DNA Repair Enzyme Polymerase theta in Cancer Therapy. Trends Cancer 7, 98–111 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

