The application of nanomedicine in clinical settings
- PMID: 37441195
- PMCID: PMC10335748
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1219054
The application of nanomedicine in clinical settings
Abstract
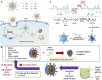
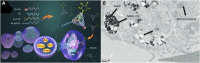
As nanotechnology develops in the fields of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, information and communication, and medical care, it has shown great promises. In recent years, medical nanorobots have made significant progress in terms of the selection of materials, fabrication methods, driving force sources, and clinical applications, such as nanomedicine. It involves bypassing biological tissues and delivering drugs directly to lesions and target cells using nanorobots, thus increasing concentration. It has also proved useful for monitoring disease progression, complementary diagnosis, and minimally invasive surgery. Also, we examine the development of nanomedicine and its applications in medicine, focusing on the use of nanomedicine in the treatment of various major diseases, including how they are generalized and how they are modified. The purpose of this review is to provide a summary and discussion of current research for the future development in nanomedicine.
Keywords: cross-disciplinary; drug delivery; micro-/nanorobots; nanomedicine; nanotechnology.
Copyright © 2023 Zhao, Cheng, Sun, Yan and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Al-Hatamleh M. A. I., Hatmal M. M., Alshaer W., Rahman E. N. S. E. A., Mohd-Zahid M. H., Alhaj-Qasem D. M., et al. (2021). COVID-19 infection and nanomedicine applications for development of vaccines and therapeutics: An overview and future perspectives based on polymersomes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 896, 173930. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173930 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

