Comparison of Rotterdam and Barcelona Magnetic Resonance Imaging Risk Calculators for Predicting Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 37441350
- PMCID: PMC10334241
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euros.2023.03.013
Comparison of Rotterdam and Barcelona Magnetic Resonance Imaging Risk Calculators for Predicting Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Background: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based risk calculators (MRI-RCs) individualise the likelihood of clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa) and improve candidate selection for prostate biopsy beyond the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS).
Objective: To compare the Barcelona (BCN) and Rotterdam (ROT) MRI-RCs in an entire population and according to the PI-RADS categories.
Design setting and participants: A prospective comparison of BCN- and ROT-RC in 946 men with suspected prostate cancer in whom systematic biopsy was performed, as well as target biopsies of PI-RADS ≥3 lesions.
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: Saved biopsies and undetected csPCa (grade group ≥2) were determined.
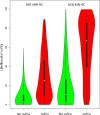
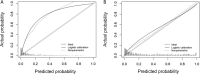
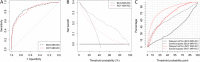
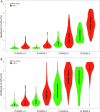
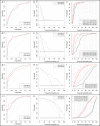
Results and limitations: The csPCa detection was 40.8%. The median risks of csPCa from BCN- and ROT-RC were, respectively, 67.1% and 25% in men with csPCa, whereas 10.5% and 3% in those without csPCa (p < 0.001). The areas under the curve were 0.856 and 0.844, respectively (p = 0.116). BCN-RC showed a higher net benefit and clinical utility over ROT-RC. Using appropriate thresholds, respectively, 75% and 80% of biopsies were needed to identify 50% of csPCa detected in men with PI-RADS <3, whereas 35% and 21% of biopsies were saved, missing 10% of csPCa detected in men with PI-RADS 3. BCN-RC saved 15% of biopsies, missing 2% of csPCa in men with PI-RADS 4, whereas ROT-RC saved 10%, missing 6%. No RC saved biopsies without missing csPCa in men with PI-RADS 5.
Conclusions: ROT-RC provided a lower and narrower range of csPCa probabilities than BCN-RC. BCN-RC showed a net benefit over ROT-RC in the entire population. However, BCN-RC was useful in men with PI-RADS 3 and 4, whereas ROT-RC was useful only in those with PI-RADS 3. No RC seemed to be helpful in men with negative MRI and PI-RADS 5.
Patient summary: Barcelona risk calculator was more helpful than Rotterdam risk calculator to select candidates for prostate biopsy.
Keywords: Clinically significant; Early detection; Magnetic resonance imaging; Predictive model; Prostate cancer; Risk calculator.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Mottet N., van den Bergh R.C.N., Briers E., et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer—2020 update. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur Urol. 2021;79:243–262. - PubMed
-
- Van Poppel H., Roobol M.J., Chapple C.R., et al. Prostate-specific antigen testing as part of a risk-adapted early detection strategy for prostate cancer: European Association of Urology position and recommendations for 2021. Eur Urol. 2021;80:703–711. - PubMed
-
- Van Poppel H., Hogenhout R., Albers P., van den Bergh R.C.N., Barentsz J.O., Roobol M.J. European model for an organised risk-stratified early detection programme for prostate cancer. Eur Urol Oncol. 2021;10:731–739. - PubMed
-
- Schoots I.G., Padhani A.R., Rouvière O., Barentsz J.O., Richenberg J. Analysis of magnetic resonance imaging-directed biopsy strategies for changing the paradigm of prostate cancer diagnosis. Eur Urol Oncol. 2020;3:32–41. - PubMed
-
- Sathianathen N.J., Omer A., Harriss E., et al. Negative predictive value of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer in the prostate imaging reporting and data system era: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol. 2020;78:402–414. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

