CircSFMBT2-OA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation through repressing NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- PMID: 37441407
- PMCID: PMC10333456
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17312
CircSFMBT2-OA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation through repressing NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Abstract
Background: Intra-articular inflammation and cartilage degradation are the major pathological characteristics of osteoarthritis (OA). Mounting studies have revealed that circular RNAs (circRNAs) act as an important regulatory role in inflammatory diseases and are frequently dys-expressed in OA cartilage tissues.
Objective: Here, a dys-regulated cicrRNA (has_circ_0017636, termed circSFMBT2-OA) was identified, and its role in regulating lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced chondrocyte injury was next investigated.
Methods: CHON-001 chondrocytes were treated with LPS, and then the levels of circSFMBT2-OA, cartilage-related genes, and pro-inflammatory cytokines were measured using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blot analysis. CHON-001 cell viability, proliferation, and apoptosis were assayed using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), 5-Ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EDU), and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay, respectively.
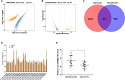
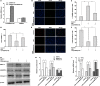
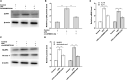
Results: CircSFMBT2-OA level was significantly down-regulated in OA cartilage tissues and LPS-treated CHON-001 cells. Functionally, circSFMBT2-OA overexpression accelerated cell proliferation, and suppressed cell apoptosis, pro-inflammatory cytokines production, matrix-degrading enzymes expression, and ECM degradation in CHON-001 cells. Inversely, circSFMBT2-OA depletion decreased cell viability and increased matrix-degrading enzymes expression and ECM degradation. Mechanistically, circSFMBT2-OA inhibited LPS-induced NF-κB/NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation in CHON-001 cells. Consequently, NLRP3 activator reversed the effect of circSFMBT2-OA on repressing LPS-induced CHON-001 cell injury.
Conclusion: These data reveal a vital effect of a novel circSFMBT2-OA on repressing OA progression and provide a promising target to treat OA.
Keywords: Chondrocyte injury; Inflammation; NLRP3; Osteoarthritis; circSFMBT2-OA.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Safiri S., Kolahi A.A., Smith E., Hill C., Bettampadi D., Mansournia M.A., Hoy D., Ashrafi-Asgarabad A., Sepidarkish M., Almasi-Hashiani A., Collins G., Kaufman J., Qorbani M., Moradi-Lakeh M., Woolf A.D., Guillemin F., March L., Cross M. Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990-2017: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020;6(79):819–828. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216515. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Global, regional And national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;10159(392):1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

