The Comparative Effectiveness of Monotherapy and Combination Therapies: Impact of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers on the Onset of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 37441415
- PMCID: PMC10333644
- DOI: 10.14283/jarlife.2023.8
The Comparative Effectiveness of Monotherapy and Combination Therapies: Impact of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers on the Onset of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background: The criteria for use of Alzheimer's disease (AD) drug Leqembi recommended by the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) include patients aged 65 years or older with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild AD. Comorbidities that include hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes are common among these patients.
Objectives: Our objective is to investigate the comparative effectiveness of the administration of one, two, or three medications belonging to the categories of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), Beta Blockers, Statins, and Metformin, for their potential to delay the clinical onset of AD and provide a window of opportunity for therapeutic intervention.
Design: Retrospective matched case-control study.
Setting: Data from the Department of Veterans Affairs national corporate data warehouse.
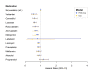
Participants: We conducted an analysis of 122,351 participants (13,611 with AD and 108,740 without AD), aged 65-89, who began at least one of the prescribed medication classes under investigation between October 1998 and April 2018.
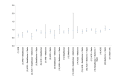
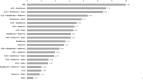
Measurements: We utilized Cox proportional hazard regressions, both with and without propensity score weighting, to estimate hazard ratios (HR) associated with the use of different medication combinations for the pre-symptomatic survival time of AD onset. Additionally, we employed a supervised machine learning algorithm (random forest) to assess the relative importance of various therapies in predicting the occurrence of AD.
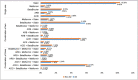
Result: Adding Metformin to the combination of ACEI+Beta Blocker (HR = 0.56, 95% CI (0.41, 0.77)) reduced the risk of AD onset compared to ACEI monotherapy alone (HR = 0.91, (0.85, 0.98)), Beta Blocker monotherapy (HR = 0.86, 95% CI (0.80, 0.92)), or combined ACEI+Beta Blocker (HR=0.85, 95%CI (0.77, 0.94)), when statin prescribers were used as a reference. Prescriptions of ARB alone or the combination of ARB with Beta Blocker showed an association with a lower risk of AD onset.
Conclusion: Selected medications for the treatment of multiple chronic conditions among elderly individuals with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes as monotherapy or combination therapies lengthen the pre-symptomatic period before the onset of AD.
Keywords: Drug repurposing; angiotensin II receptor blocker; angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; beta blocker; combination therapy; metformin; statin.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors confirm there is no conflict of interest for the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- van Dyck, C. H., Swanson C. J., Aisen P., Bateman R. J., Chen C., Gee M., Kanekiyo M., Li D., Reyderman L., Cohen S., Froelich L., Katayama S., Sabbagh M., Vellas B., Watson D., Dhadda S.,Irizarry M., Kramer L. D. and Iwatsubo T.. “Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease.” New England Journal of Medicine 2022;388(1): 9-21, 10.1056/NEJMoa2212948 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cummings, J., Apostolova L., Rabinovici G. D., Atri A., Aisen P., Greenberg S., Hendrix S., Selkoe D., Weiner M., Petersen R. C., Salloway S., D. For the Alzheimer’s and G. Related Disorders Therapeutics Work. “Lecanemab: Appropriate Use Recommendations.” The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease, 2023: 10.14283/jpad.12023.14230 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
