Intrinsic mechanism and pharmacologic treatments of noise-induced hearing loss
- PMID: 37441605
- PMCID: PMC10334830
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.83383
Intrinsic mechanism and pharmacologic treatments of noise-induced hearing loss
Abstract
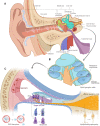
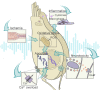
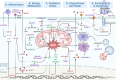
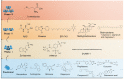
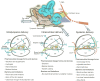
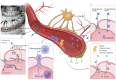
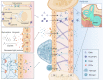
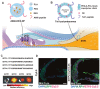
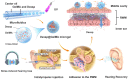
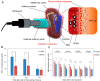
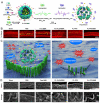
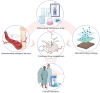
Noise accounts for one-third of hearing loss worldwide. Regretfully, noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is deemed to be irreversible due to the elusive pathogenic mechanisms that have not been fully elucidated. The complex interaction between genetic and environmental factors, which influences numerous downstream molecular and cellular events, contributes to the NIHL. In clinical settings, there are no effective therapeutic drugs other than steroids, which are the only treatment option for patients with NIHL. Therefore, the need for treatment of NIHL that is currently unmet, along with recent progress in our understanding of the underlying regulatory mechanisms, has led to a lot of new literatures focusing on this therapeutic field. The emergence of novel technologies that modify local drug delivery to the inner ear has led to the development of promising therapeutic approaches, which are currently under clinical investigation. In this comprehensive review, we focus on outlining and analyzing the basics and potential therapeutics of NIHL, as well as the application of biomaterials and nanomedicines in inner ear drug delivery. The objective of this review is to provide an incentive for NIHL's fundamental research and future clinical translation.
Keywords: drug delivery systems; nanoparticles; noise-induced hearing loss; pharmacologic strategies.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Varela-Nieto I, Murillo-Cuesta S, Calvino M, Cediel R, Lassaletta L. Drug development for noise-induced hearing loss. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2020;15:1457–71. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Shi L, Liu L, Yin S, Aiken S, Wang J. Noise-induced cochlear synaptopathy and signal processing disorders. Neuroscience. 2019;407:41–52. - PubMed
-
- Virkkunen H, Kauppinen T, Tenkanen L. Long-term effect of occupational noise on the risk of coronary heart disease. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2005;31:291–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

