Bilateral lung transplantation for pediatric pulmonary arterial hypertension: perioperative management and one-year follow-up
- PMID: 37441704
- PMCID: PMC10333590
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1193326
Bilateral lung transplantation for pediatric pulmonary arterial hypertension: perioperative management and one-year follow-up
Abstract
Background: Bilateral lung transplantation (LuTx) remains the only established treatment for children with end-stage pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Although PAH is the second most common indication for LuTx, little is known about optimal perioperative management and midterm clinical outcomes.
Methods: Prospective observational study on consecutive children with PAH who underwent LuTx with scheduled postoperative VA-ECMO support at Hannover Medical School from December 2013 to June 2020.
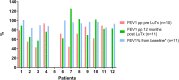
Results: Twelve patients with PAH underwent LuTx (mean age 11.9 years; age range 1.9-17.8). Underlying diagnoses included idiopathic (n = 4) or heritable PAH (n = 4), PAH associated with congenital heart disease (n = 2), pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (n = 1), and pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis (n = 1). The mean waiting time was 58.5 days (range 1-220d). Three patients were bridged to LuTx on VA-ECMO. Intraoperative VA-ECMO/cardiopulmonary bypass was applied and VA-ECMO was continued postoperatively in all patients (mean ECMO-duration 185 h; range 73-363 h; early extubation). The median postoperative ventilation time was 28 h (range 17-145 h). Echocardiographic conventional and strain analysis showed that 12 months after LuTx, all patients had normal biventricular systolic function. All PAH patients are alive 2 years after LuTx (median follow-up 53 months, range 26-104 months).
Conclusion: LuTx in children with end-stage PAH resulted in excellent midterm outcomes (100% survival 2 years post-LuTx). Postoperative VA-ECMO facilitates early extubation with rapid gain of allograft function and sustained biventricular reverse-remodeling and systolic function after RV pressure unloading and LV volume loading.
Keywords: awake ECMO; children; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO); lung transplantation; pediatric; pulmonary arterial hypertension.
© 2023 Jack, Carlens, Diekmann, Hasan, Chouvarine, Schwerk, Müller, Wieland, Tudorache, Warnecke, Avsar, Horke, Ius, Bobylev and Hansmann.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor SM declared a shared committee working group lung transplantation with the author FI at the time of review.
Figures


References
-
- Hansmann G, Koestenberger M, Alastalo TP, Apitz C, Austin ED, Bonnet D, et al. 2019 updated consensus statement on the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric pulmonary hypertension: the European pediatric pulmonary vascular disease network (EPPVDN), endorsed by AEPC, ESPR and ISHLT. J Heart Lung Transplant. (2019) 38:879–901. 10.1016/j.healun.2019.06.022 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

