Levels and clinical significance of the m6A methyltransferase METTL14 in patients with coronary heart disease
- PMID: 37441706
- PMCID: PMC10333499
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1167132
Levels and clinical significance of the m6A methyltransferase METTL14 in patients with coronary heart disease
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the association of methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) expression with coronary heart disease (CHD).
Methods: Three hundred and sixteen patients who attended Henan Provincial People's Hospital between June 2019 and February 2021 with principal symptoms of pain or tightness in the chest and who underwent coronary angiography for definitive diagnosis were enrolled. The uric acid, TG, TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, apolipoprotein A1, free fatty acid, lipoprotein a, homocysteine, CRP, and SAA levels were examined. The levels of METTL14, TNF-α, MCP-1, VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and IL-6 were evaluated by ELISA.
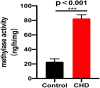
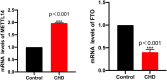
Results: Patients with CHD had significantly higher m6A methyltransferase activity. In addition, the incidence of diabetes and hypertension, as well as the concentrations of TC, CRP, and SAA were higher in CHD patients. Patients with coronary lesion branches also had significantly increased TG, LDL-C, CRP, and SAA levels. TNF-α, MCP-1, VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and IL-6 expression was also markedly increased in the CHD group (P < 0.001) as was the expression of METTL14 (P < 0.001). The METTL14 expression levels also differed significantly in relation to the number of branches with lesions (P < 0.01) and were correlated with SAA, VCAM-1, ICAM-1, IL-6, and the Gensini score. ROC curve analyses of METTL14 in CHD indicated an AUC of 0.881 (0.679, 0.894) with a cut-off value of 342.37, a sensitivity of 77%, and a specificity of 84%. MCP-1, VCAM-1, IL-6, SAA, and METTL14 were found to independently predict CHD risk.
Conclusions: METTL14 levels were found to be positively associated with inflammatory markers and to be an independent predictor of CHD risk.
Keywords: METTL14; atherosclerosis; coronary heart disease; inflammatory markers; m6A methylation.
© 2023 Guo, He, Hu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical significance of the m6A methyltransferase METTL3 in peripheral blood of patients with coronary heart disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Sep 20;11:1442098. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1442098. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39371395 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of Long Non-coding RNA LncRNA-FA2H-2 With Inflammatory Markers in the Peripheral Blood of Patients With Coronary Heart Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jun 21;8:682959. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.682959. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34235188 Free PMC article.
-
[Relationship between serum levels of osteoproteins, inflammatory cytokines and coronary heart disease and disease severity].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 May;31(5):588-593. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.05.013. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31198145 Chinese.
-
Association between serum amyloid A levels and coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 26 studies.Inflamm Res. 2020 Apr;69(4):331-345. doi: 10.1007/s00011-020-01325-1. Epub 2020 Feb 22. Inflamm Res. 2020. PMID: 32088731
-
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and atherosclerotic disease: from improved risk prediction to risk-guided therapy.Int J Cardiol. 2013 Oct 15;168(6):5126-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.07.113. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Int J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23978367 Review.
Cited by
-
N6-methyladenosine RNA landscape in the aged mouse hearts.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jun 18;12:1563364. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1563364. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40606020 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of m6 A methylation in coronary heart disease.J Mol Med (Berl). 2025 Jun;103(6):619-633. doi: 10.1007/s00109-025-02540-1. Epub 2025 Apr 10. J Mol Med (Berl). 2025. PMID: 40208302 Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine modification in ischemic stroke: Functions, regulation, and therapeutic potential.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 23;10(3):e25192. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25192. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38317953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL16 Contributes to Coronary Heart Disease by Inducing TET2 m6A Modification.J Inflamm Res. 2025 May 27;18:6821-6830. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S487828. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40453970 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of the m6A methyltransferase METTL3 in peripheral blood of patients with coronary heart disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Sep 20;11:1442098. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1442098. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39371395 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous